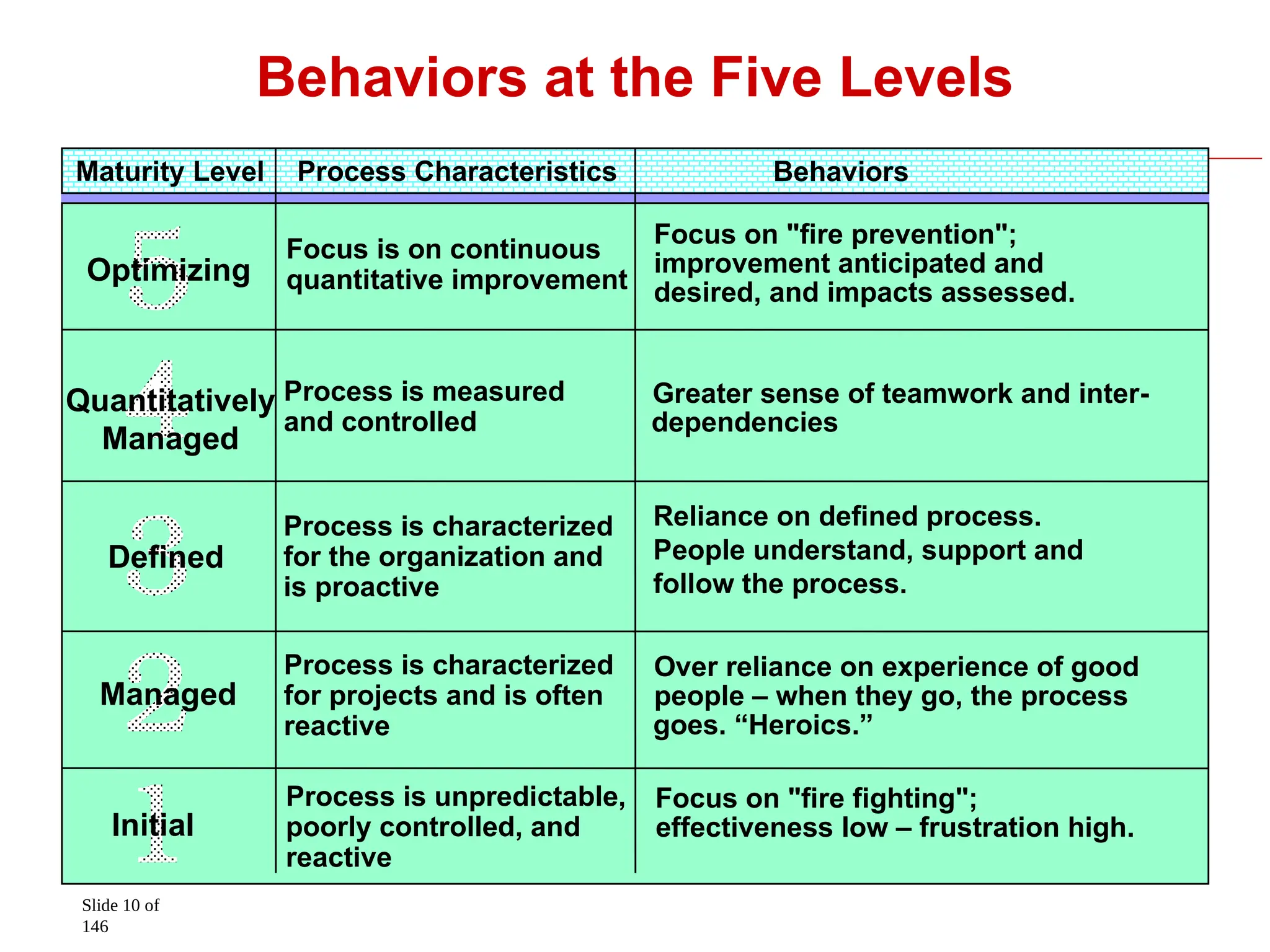
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) is a framework aimed at improving product quality and development efficiency for both hardware and software, established by the U.S. Department of Defense in collaboration with Carnegie Mellon University. It describes five maturity levels to help organizations enhance their processes, requiring significant investment but promising increased efficiency and quality over time. CMMI interfaces well with other standards, such as ISO/TL9000, and emphasizes the importance of behavioral changes at all levels within an organization.