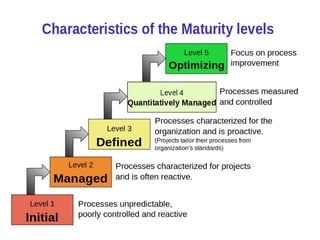
The document provides an overview of the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), outlining its purpose to improve product quality and development efficiency through five maturity levels. It describes the characteristics, goals, practices, and benefits of CMMI, emphasizing the need for structured processes in software development and project management. Achieving CMMI level 3 is presented as a significant milestone indicating the organization's maturity and ability to deliver value to customers.