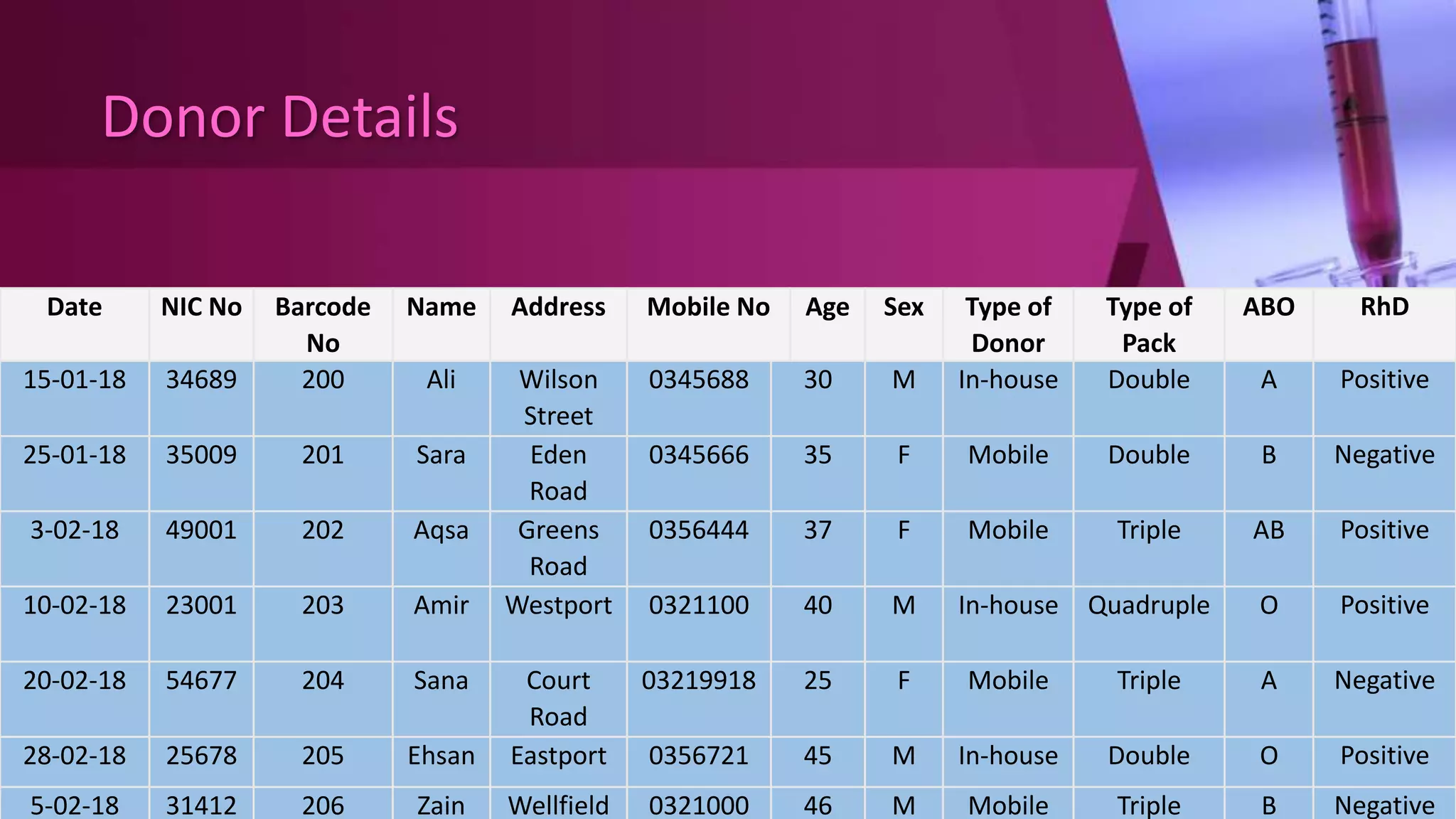
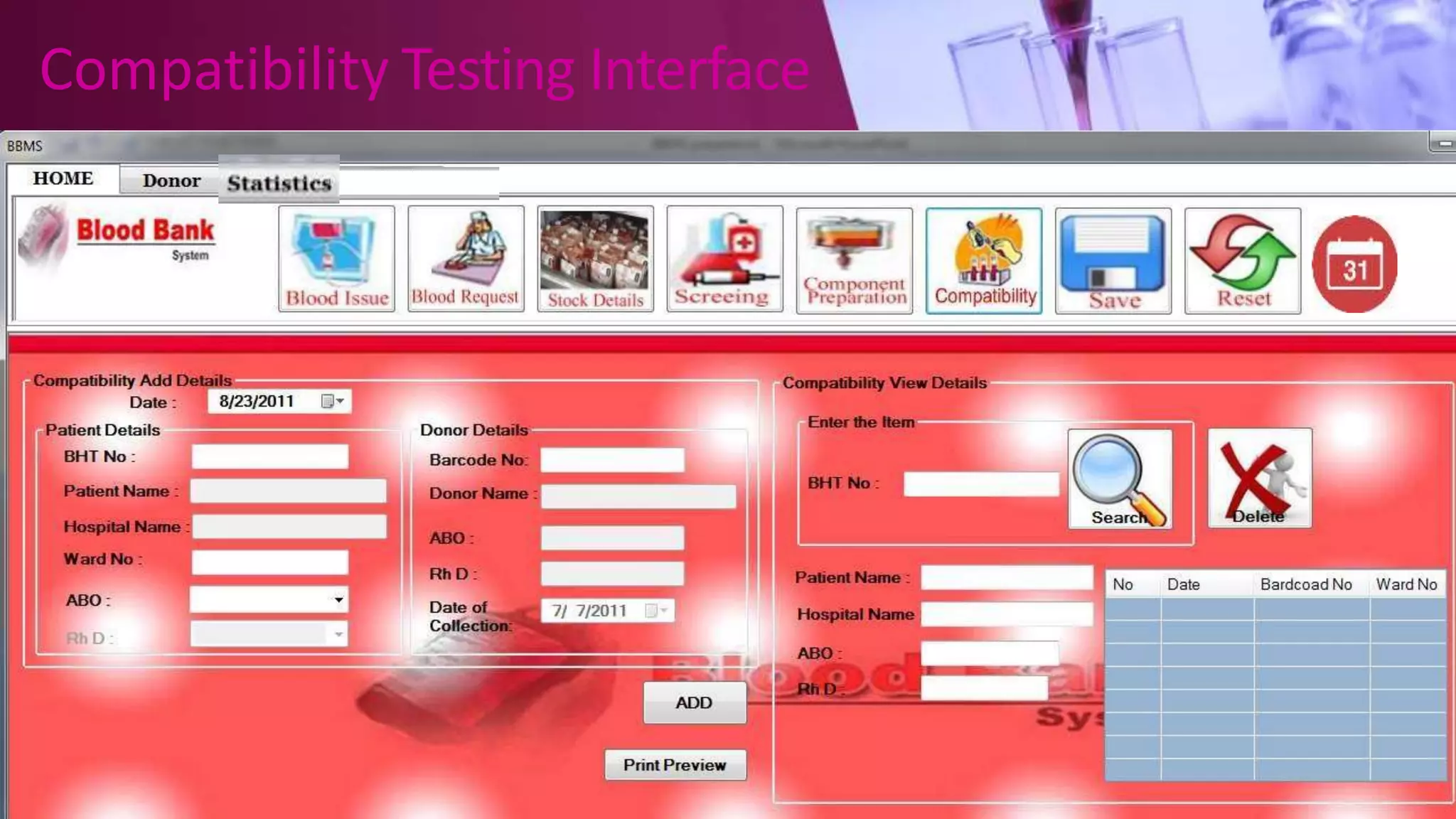
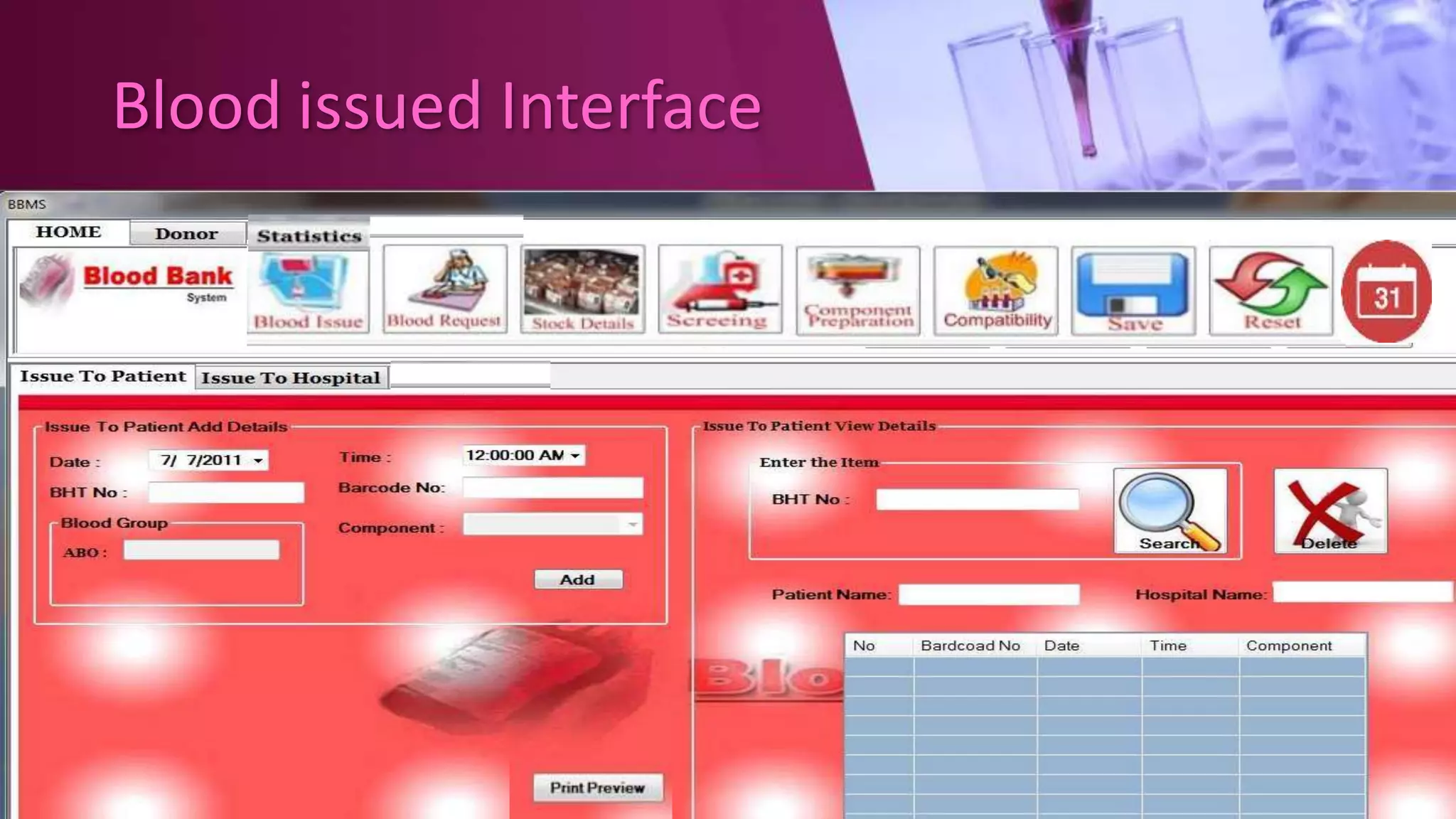
This document describes a blood bank management system with four main modules: administration, donor, receiver, and activities. The system is designed to gather blood from various sources, distribute it to hospitals and those in need, and manage the database. It allows users to track donor details, blood collection, screening, component preparation, storage, requests, compatibility testing, issue blood, and generate monthly statistics. The system provides functionality to efficiently manage all processes within the blood bank.