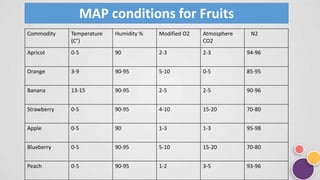
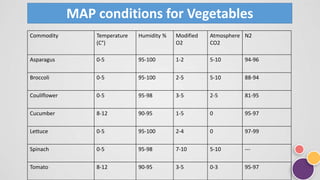
The document discusses modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), a technique that alters the internal atmosphere of food packages to extend shelf life by reducing spoilage mechanisms such as oxidation, bacterial action, and mold growth. It outlines the main gases used in MAP, the methods of passive and active packaging, and provides specific atmospheric conditions for various fruits and vegetables. The advantages of MAP include improved food quality and extended shelf life, while disadvantages include high costs and potential risks of food-borne pathogens.