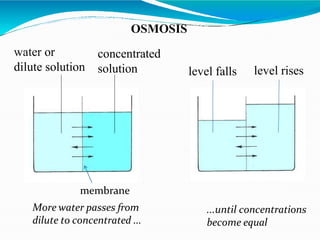
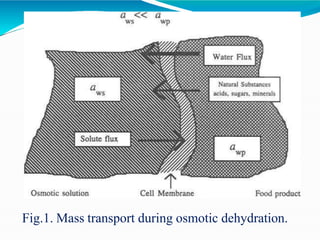
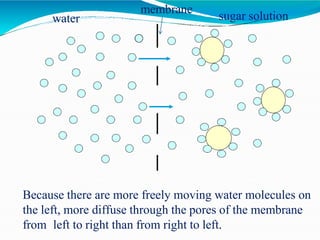
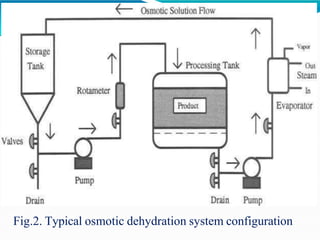
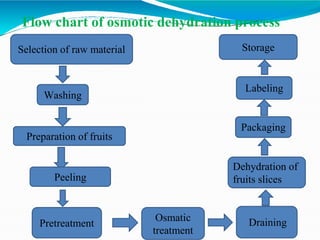
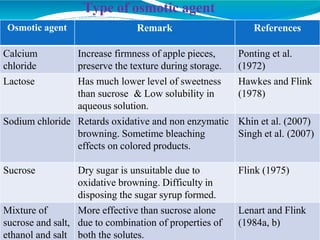
Osmotic dehydration is a process where water is removed from foods through immersion in a concentrated solution, resulting in three simultaneous flows - water diffusion into the solution, solute diffusion into the food, and leaching of food solutes. It provides several advantages over air drying like better retention of quality attributes, nutrients, and flavors. The key factors affecting osmotic dehydration rates are the type and concentration of osmotic agent, treatment time and temperature, and size and geometry of the food. Pretreatments like blanching or high pressure processing and combining it with techniques like microwave or vacuum drying can further enhance its effectiveness.