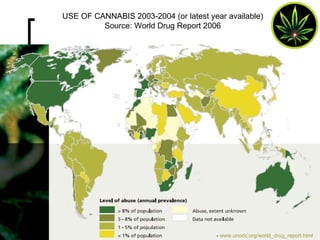
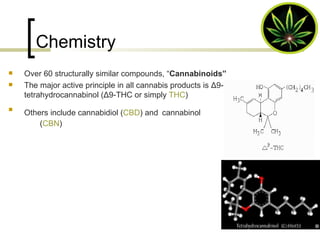
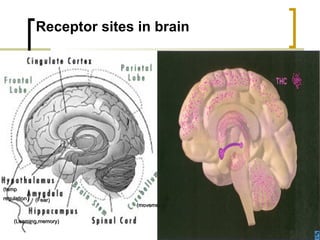
Cannabis, also known as marijuana, is the most widely used illicit drug in the world with approximately 4% of the world's adults using it annually. It comes from the Cannabis sativa plant and contains the active chemical THC. Common forms of cannabis include herbal cannabis, marijuana, bhang, ganja, charas, and hashish oil. Cannabis acts on receptors in the brain to produce effects like relaxation and impaired coordination. Long term effects can include impaired cognitive skills and increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Short term effects include anxiety, paranoia, and hallucinations. Cannabis is identified through microscopic examination and color tests.