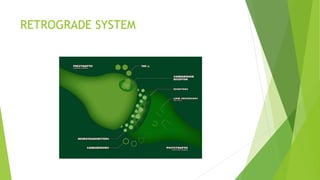
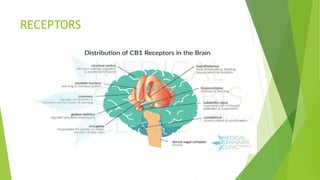
This document provides an overview of marijuana, including what it is, its sources, common street names, how it is produced and used, its mechanism of action in the body, potential medical uses and side effects, and approaches to managing addiction. Marijuana comes from the Cannabis plant and contains compounds like THC that interact with the endocannabinoid system in the brain. Common short-term side effects include impaired memory and judgment, anxiety, and depression, while long-term use has been linked to poorer life outcomes. Treatment for marijuana addiction typically involves behavioral therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy and motivational enhancement therapy.