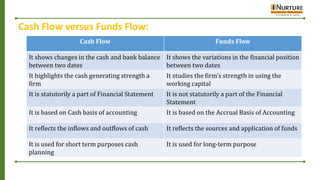
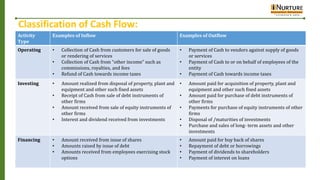
The document provides an overview of cash flow statements including their meaning, objectives, advantages, disadvantages and classification of cash flows. It explains that cash flow statements reveal movements in cash from operating, investing and financing activities. The objectives are to understand liquidity, impact of activities and cash earning capacity. Cash flows are classified as operating, investing or financing depending on the nature of transaction.