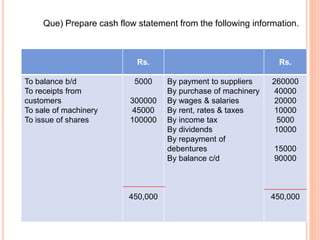
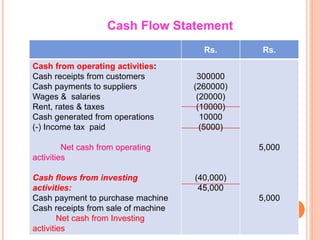
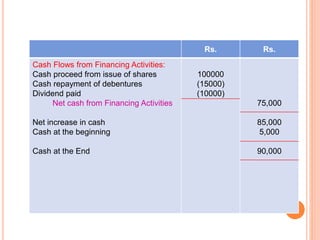
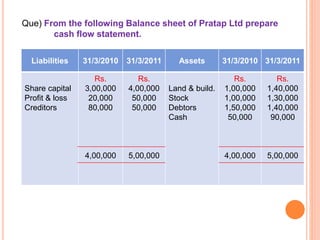
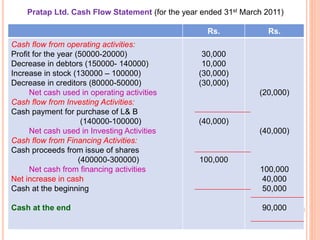
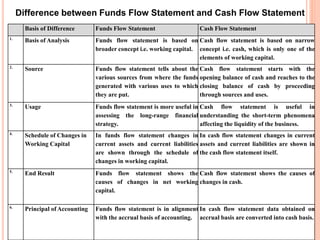
The document provides information about cash flow statements, including:
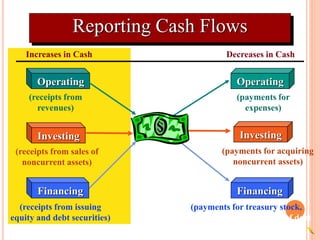
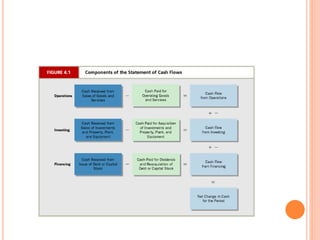
1. Cash flow statements show the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents over a period of time for operating, investing, and financing activities.
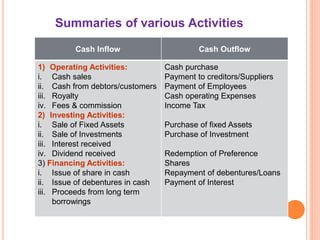
2. Operating activities include principal revenue-generating activities and other day-to-day activities. Investing activities involve the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets. Financing activities involve activities that alter ownership equity and borrowing.
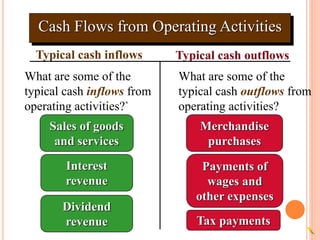
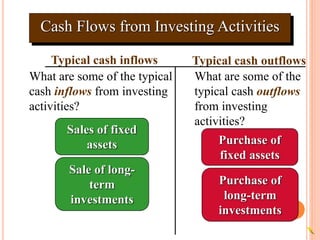
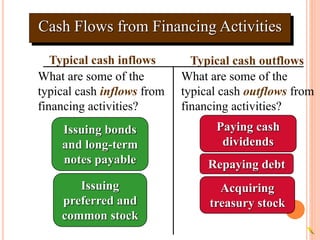
3. Typical cash inflows for operating activities include cash sales and collections from customers. Typical cash outflows are payments to suppliers and employees. For investing, typical cash inflows are from asset sales and typical cash outflows are for asset purchases. For financing,