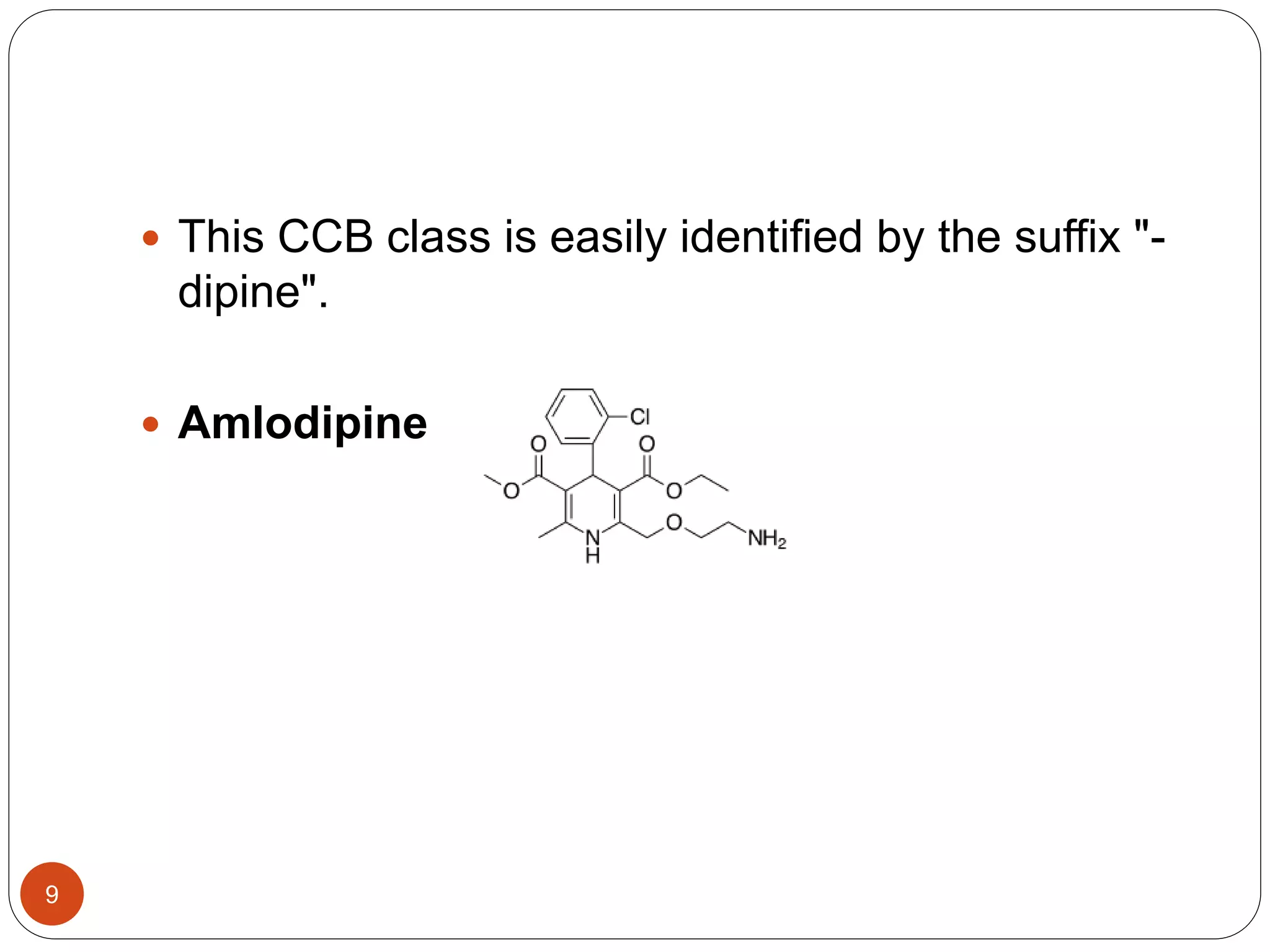
This document discusses calcium channel blockers (CCBs). It begins with an introduction to CCBs, noting they were first identified in 1964 and disrupt the movement of calcium ions into cells. It then discusses the mechanism of action of CCBs in preventing calcium channels from opening and reducing intracellular calcium levels. Examples of CCB classes are provided, including dihydropyridines like nifedipine, and phenylalkylamines like verapamil. The document concludes by stating CCBs are used to reduce blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance.