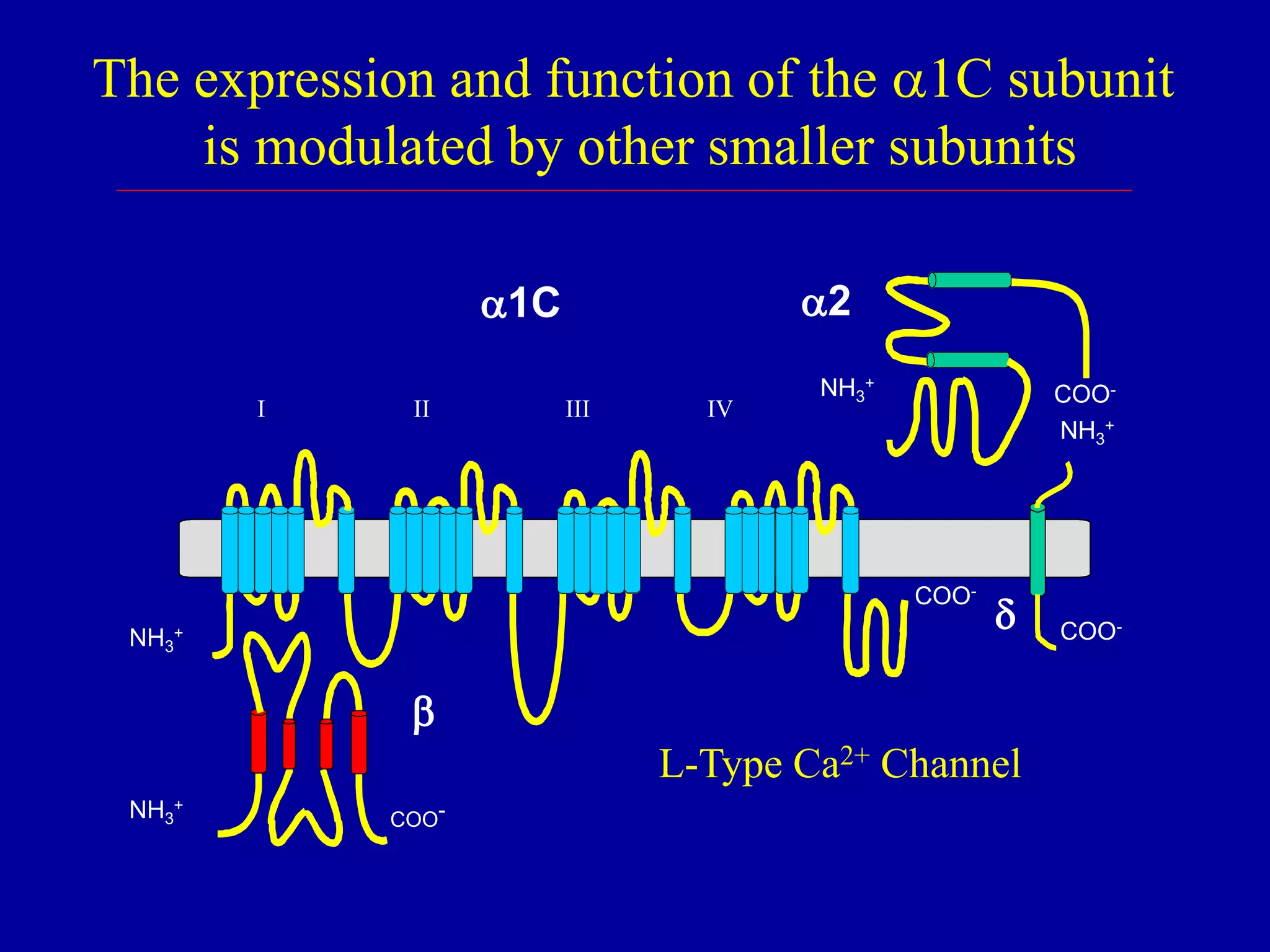
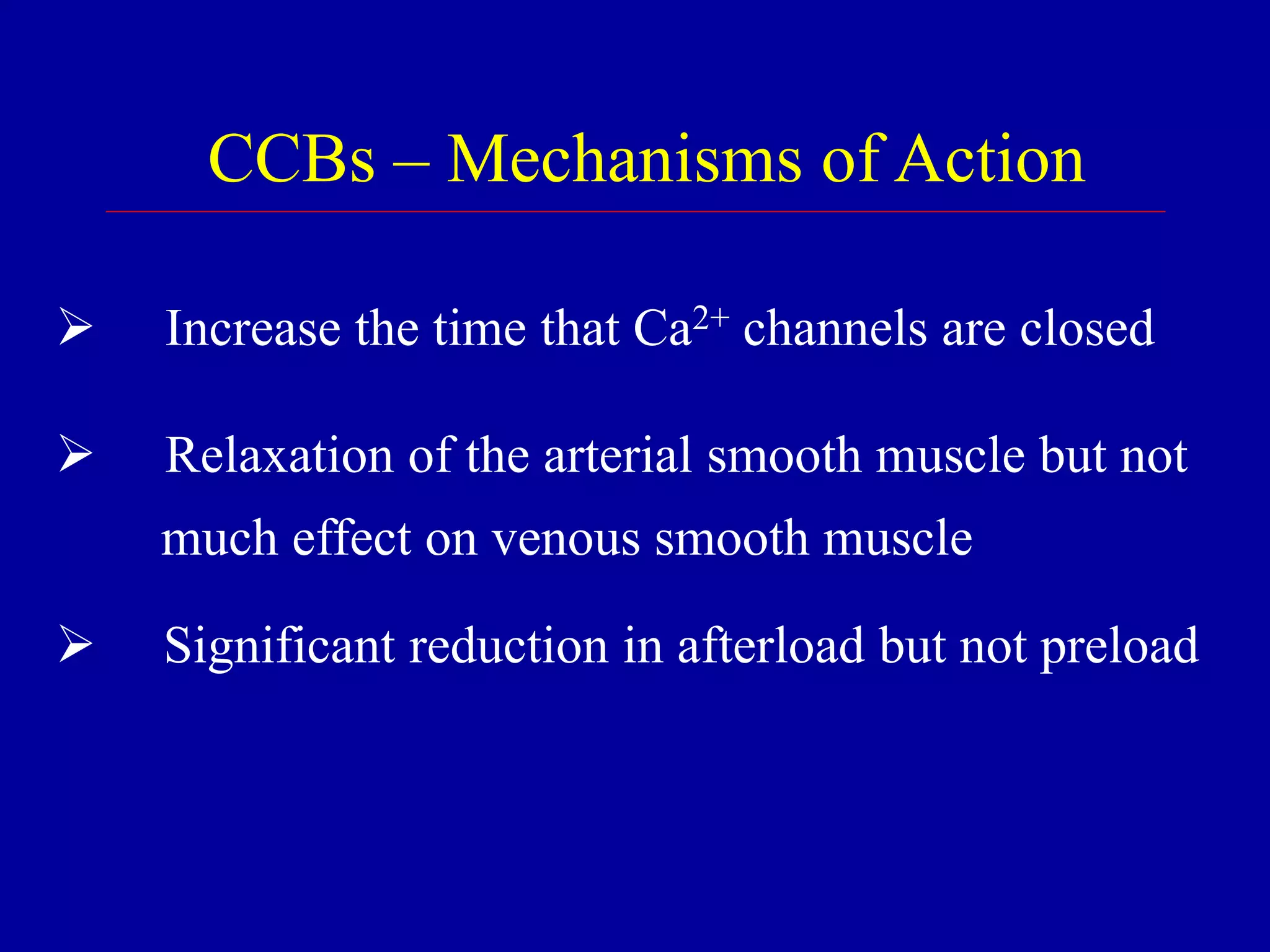
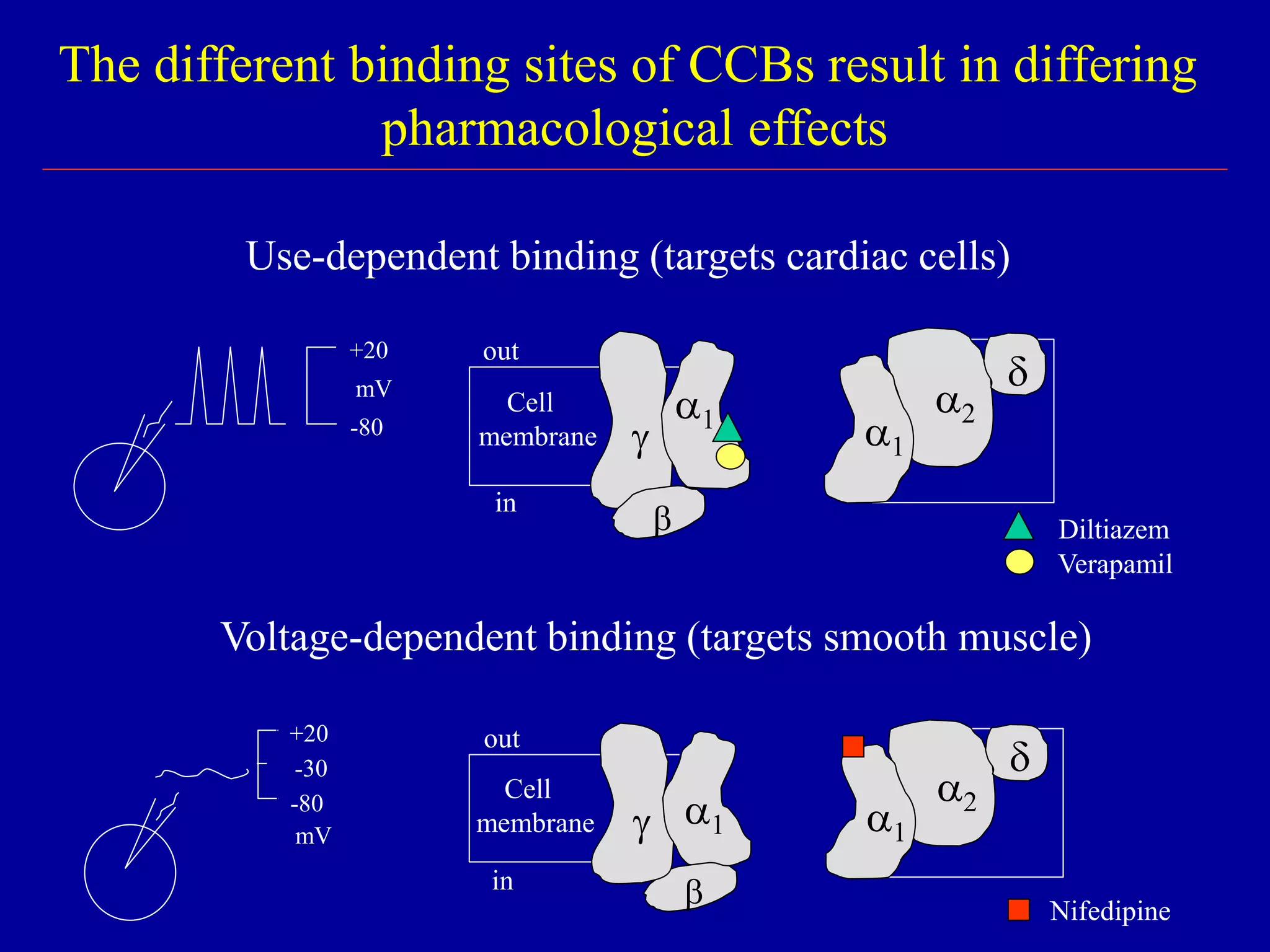
The document discusses calcium channel blocking (CCB) drugs. It describes the three classes of CCBs - phenylalkylamines, benzothiazepines, and dihydropyridines - and how they bind to different sites on L-type calcium channels. This binding selectivity allows CCBs to differentially affect cardiac and vascular muscle. The document outlines CCB pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, contraindications, and how the classes compare in these areas. It explains how CCBs can improve cardiac function by reducing afterload on the heart without affecting contractility or preload.










![CCBs Act Selectively on Cardiovascular Tissues
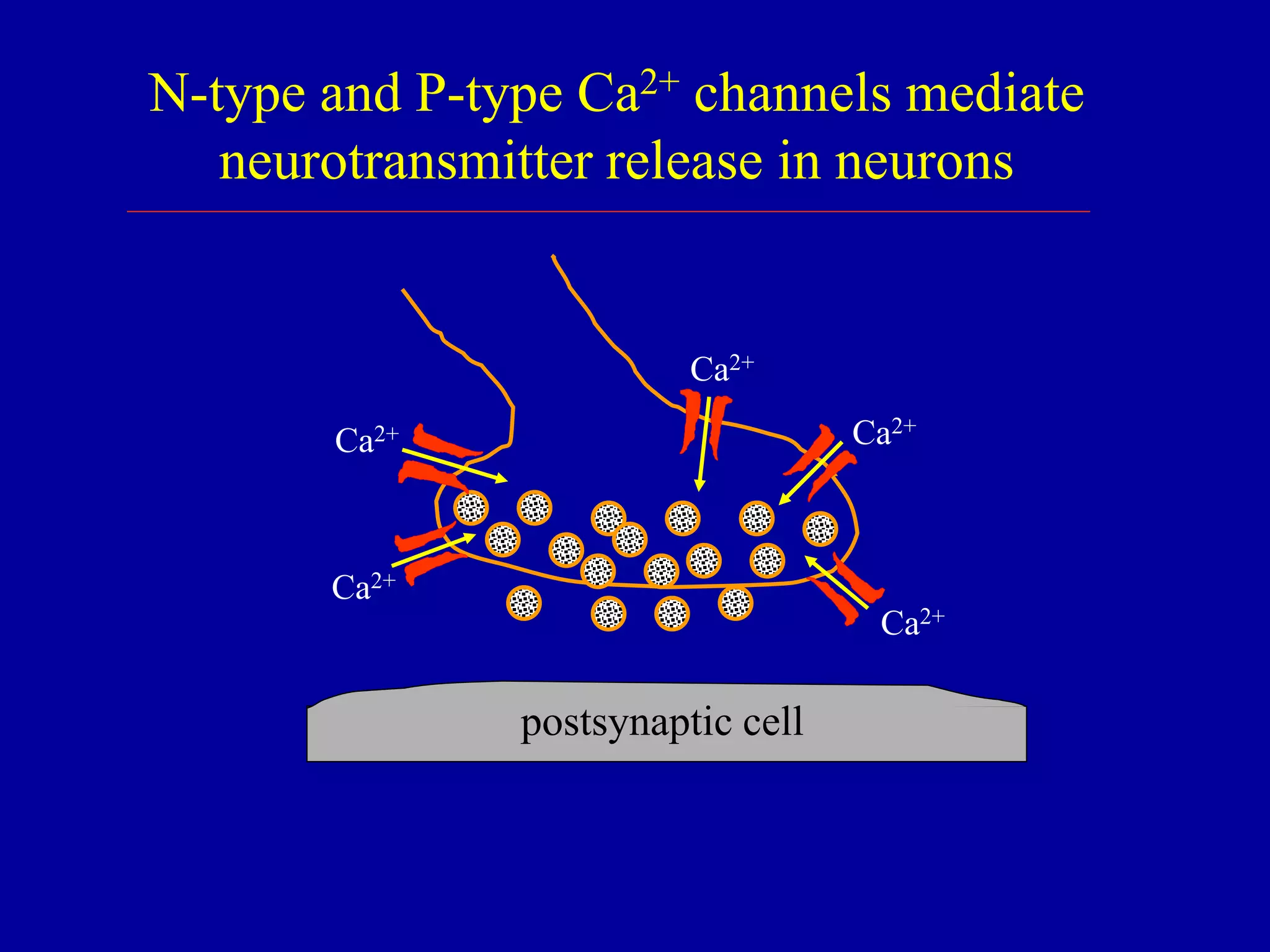
Neurons rely on N-and P-type Ca2+ channels
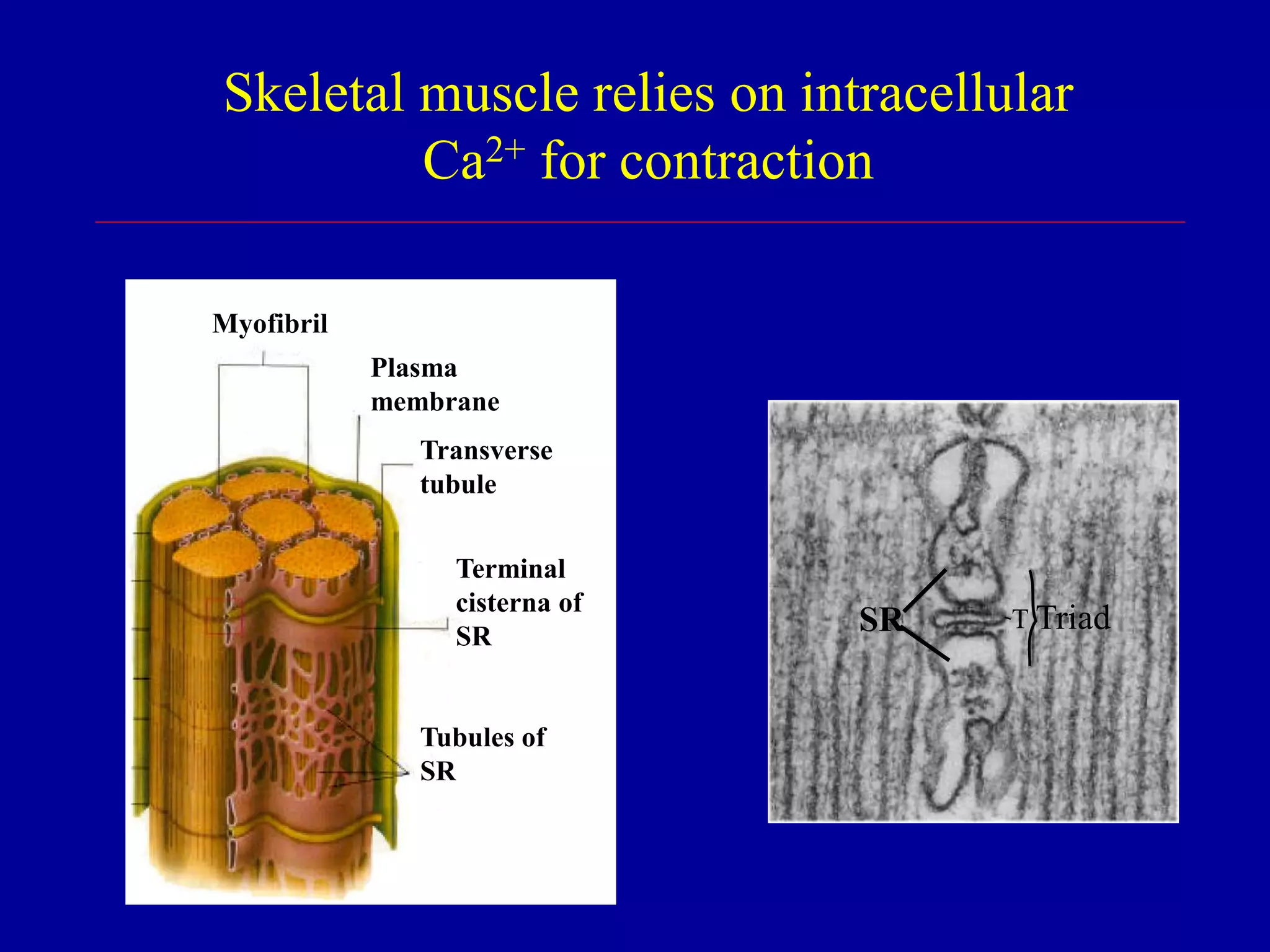
Skeletal muscle relies primarily on [Ca]i
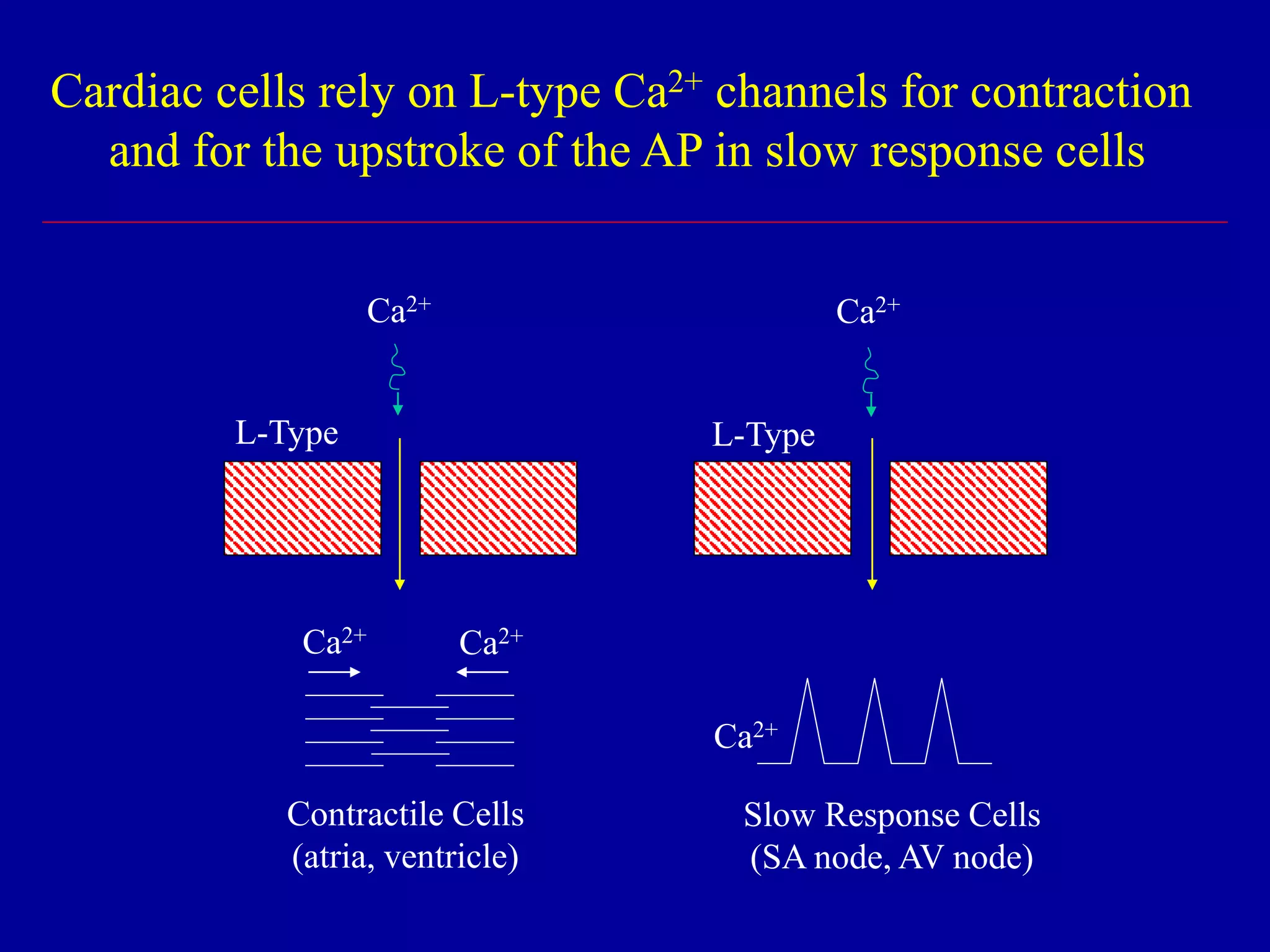
Cardiac muscle requires Ca2+ influx through
L-type Ca2+ channels
- contraction (fast response cells)
- upstroke of AP (slow response cells)
Vascular smooth muscle requires Ca2+ influx
through L-type Ca2+ channels for contraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumchannelblockers1-151207045532-lva1-app6892/75/Calcium-channel-blockers-1-18-2048.jpg)