Embed presentation
Download to read offline



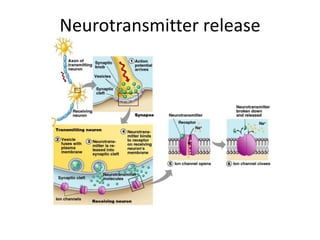




This document discusses drugs that act on the autonomic nervous system. It explains that there are two main types of cholinergic drugs: direct-acting cholinergic agonists that bind directly to cholinergic receptors, and indirect-acting cholinergic agonists that inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase to prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine. Examples of each type are provided, including direct agonists like acetylcholine and indirect agonists like physostigmine. The document aims to help students understand neurotransmitter release and the differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.






