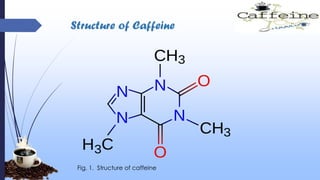
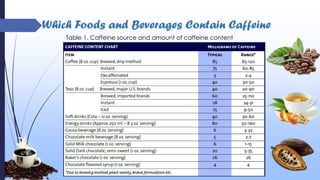
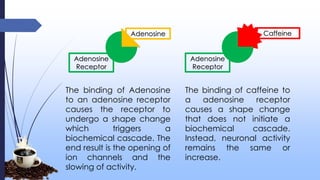
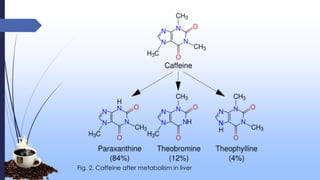
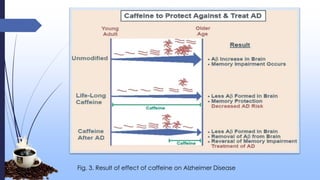
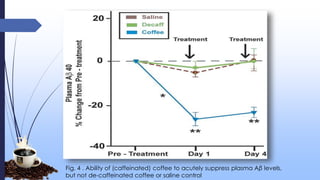
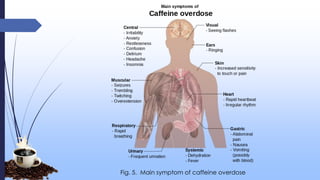
This document discusses caffeine, including its history, sources, mechanism of action, metabolism, extraction processes, health benefits, risks, and decaffeination. Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in coffee, tea, soft drinks and energy drinks. It acts as an antagonist to adenosine receptors in the brain, increasing neuronal activity. While caffeine has potential benefits like reducing Alzheimer's risk, it can also increase heart rate and blood pressure. The document examines studies on both the positive and negative health effects of caffeine consumption.