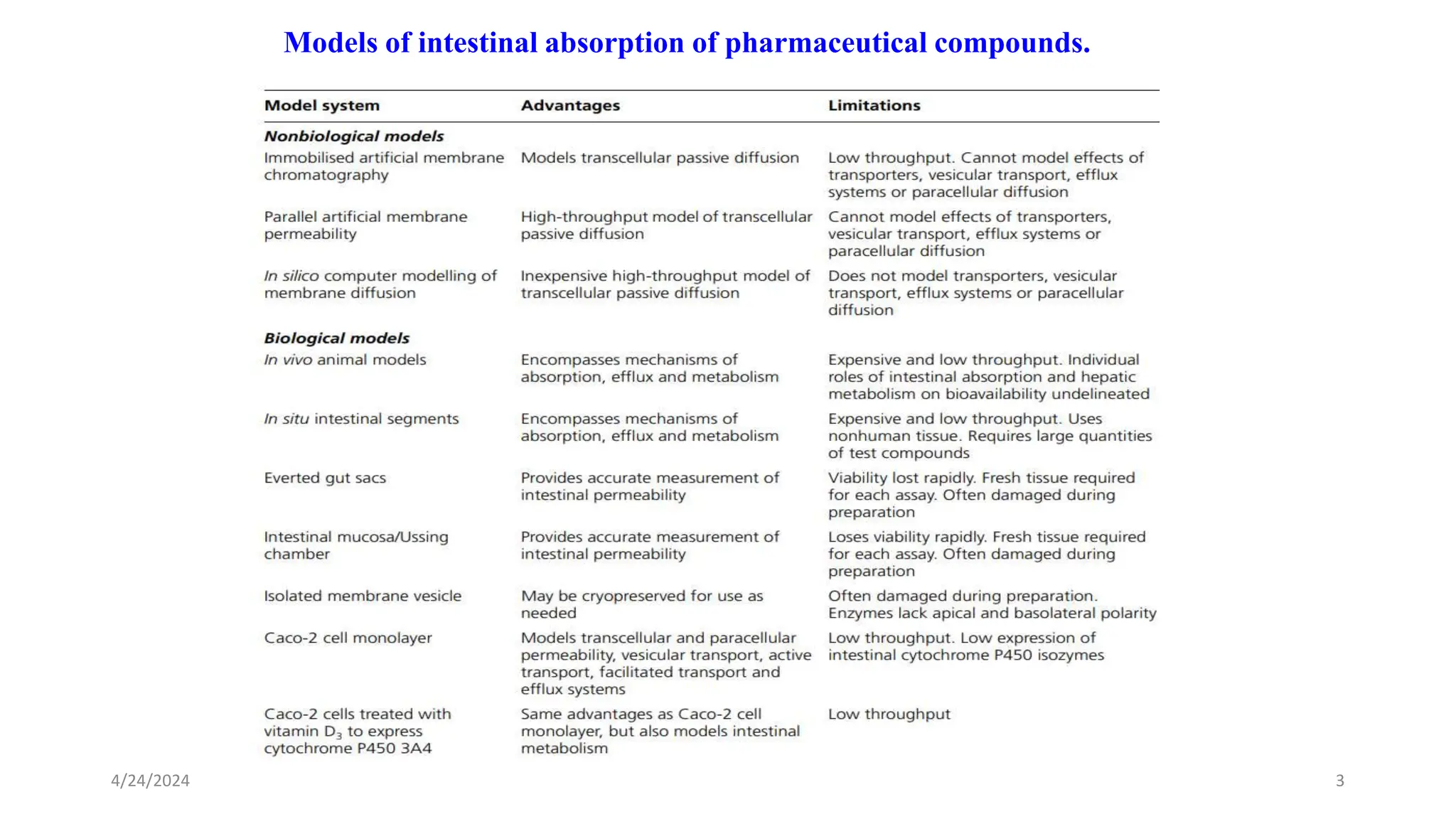
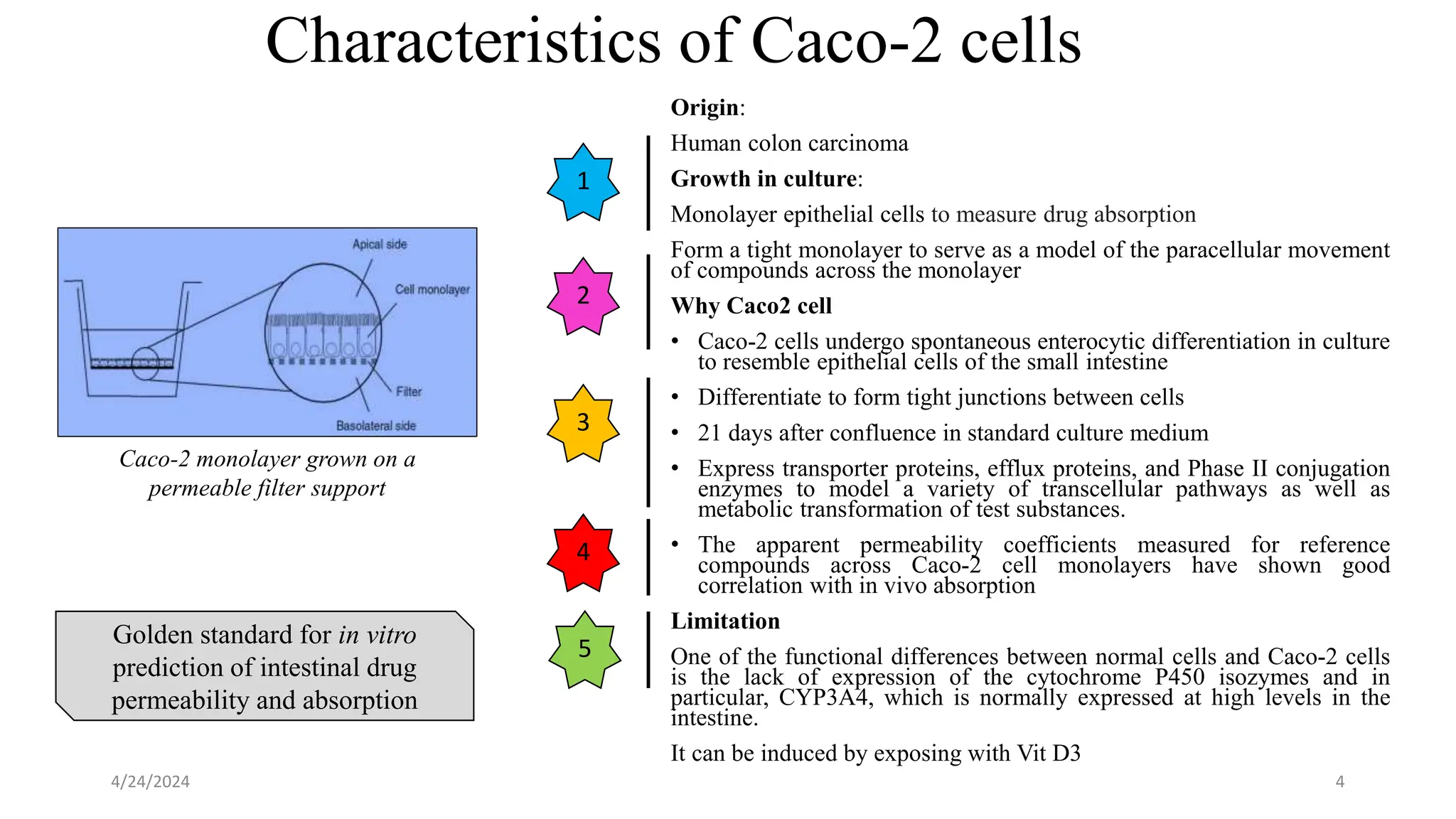
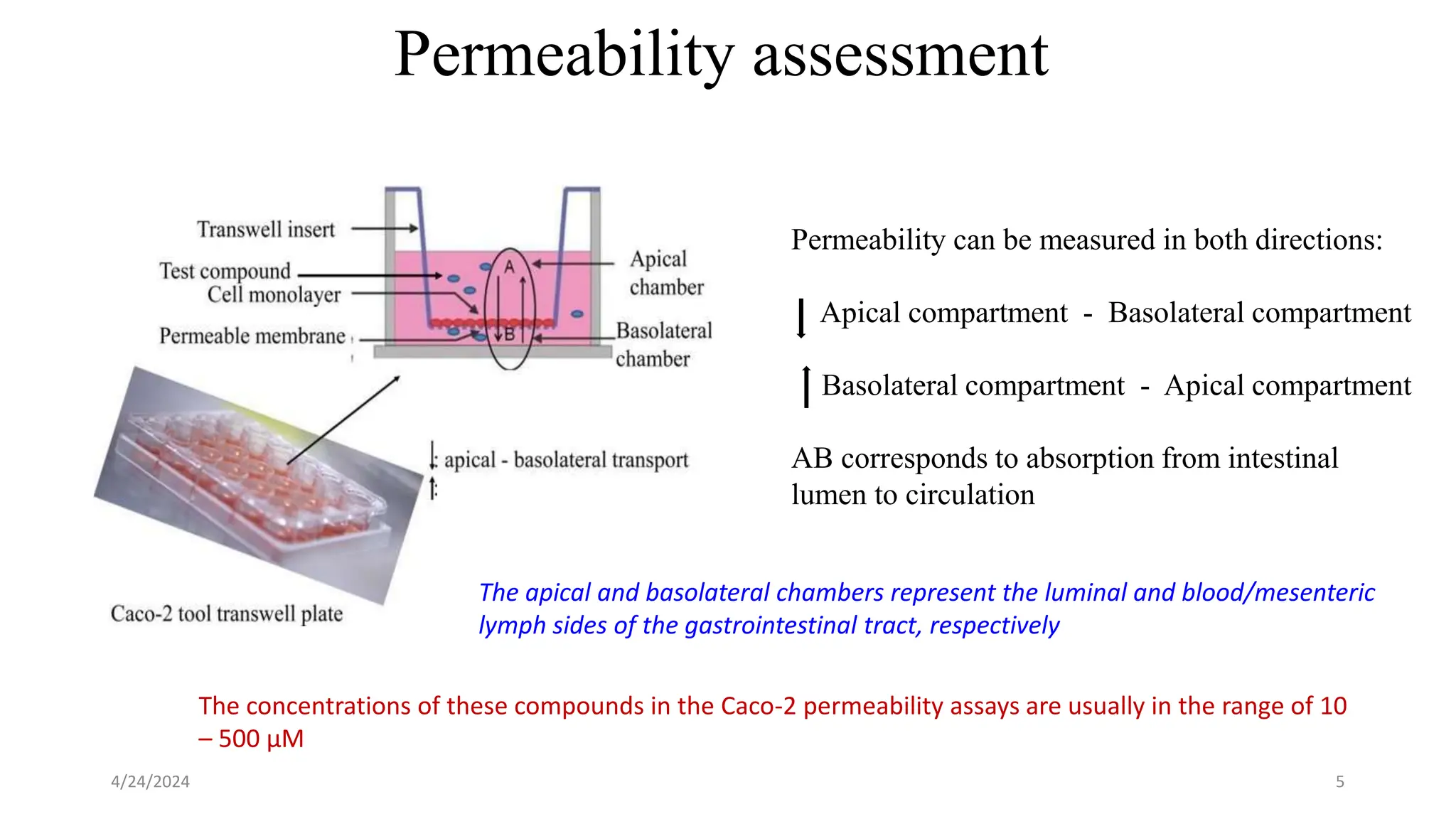
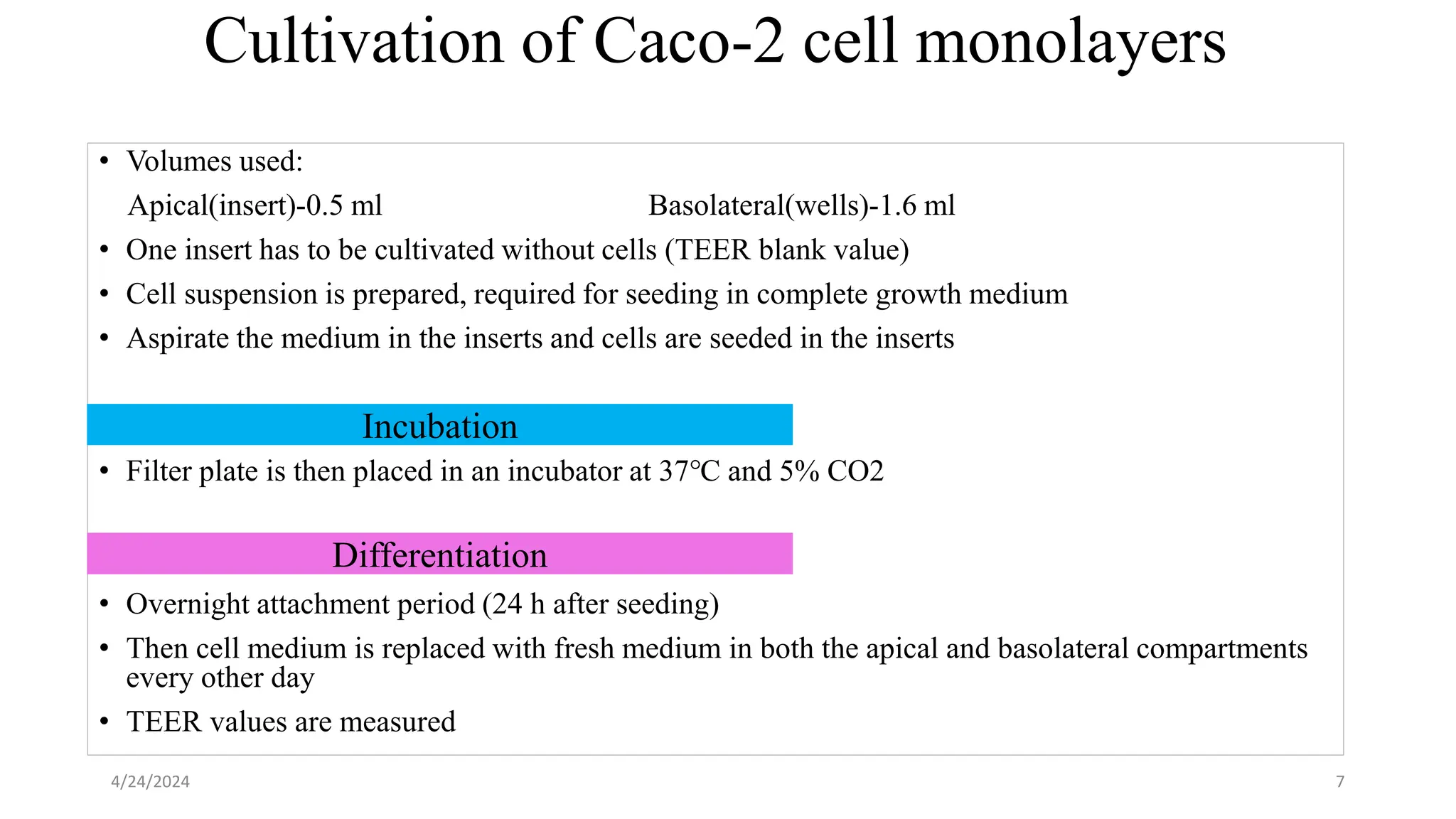
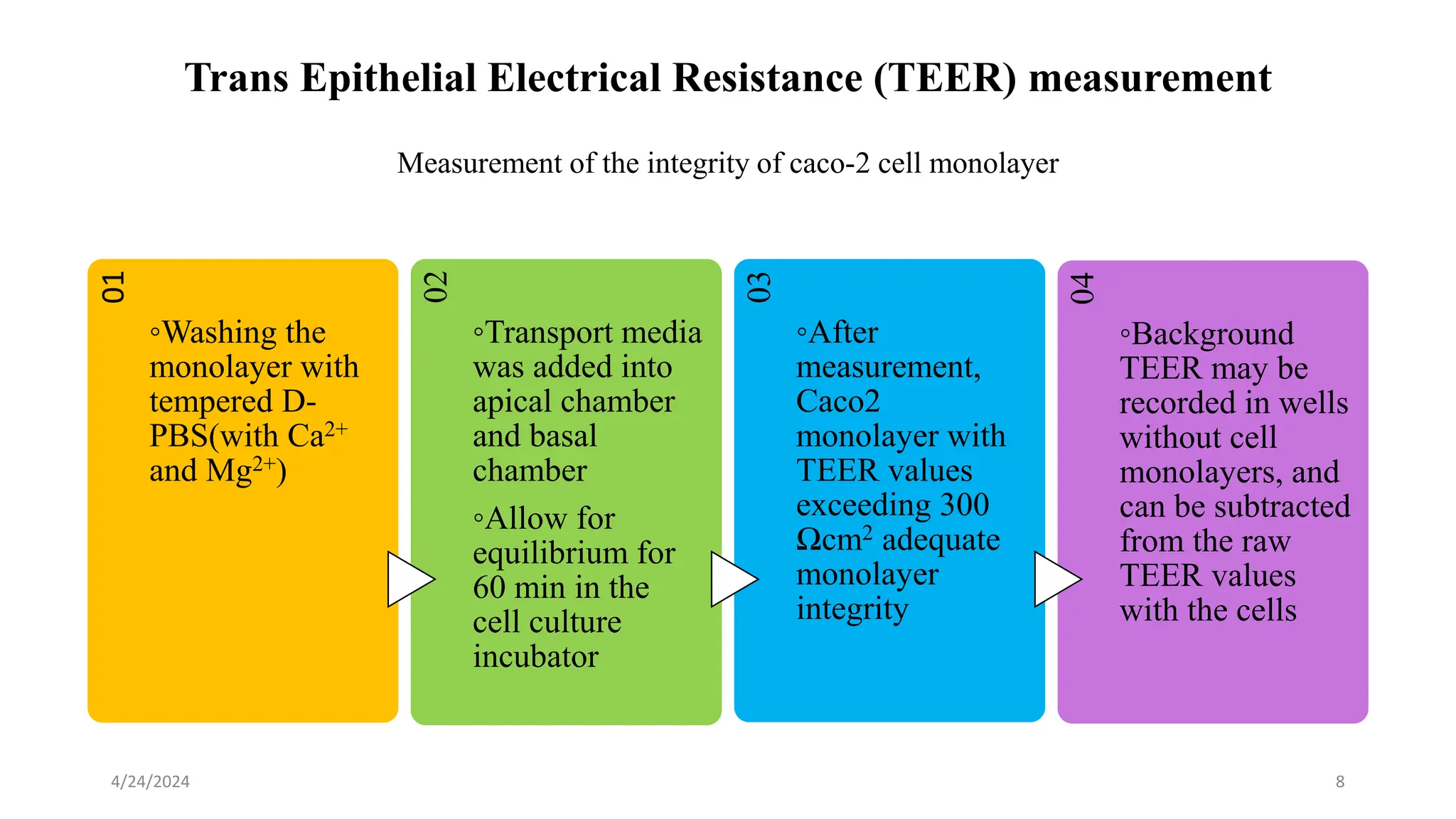
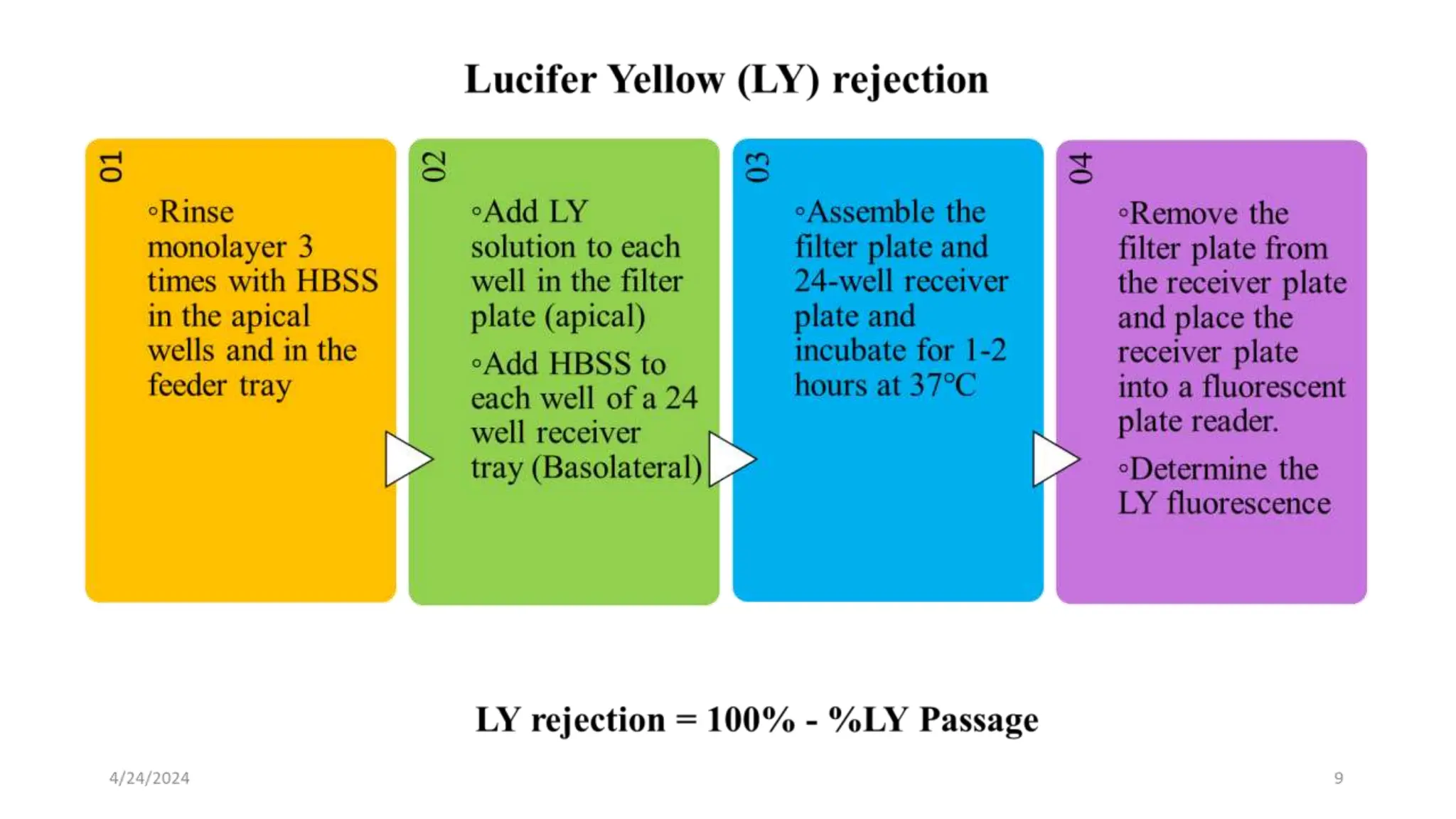
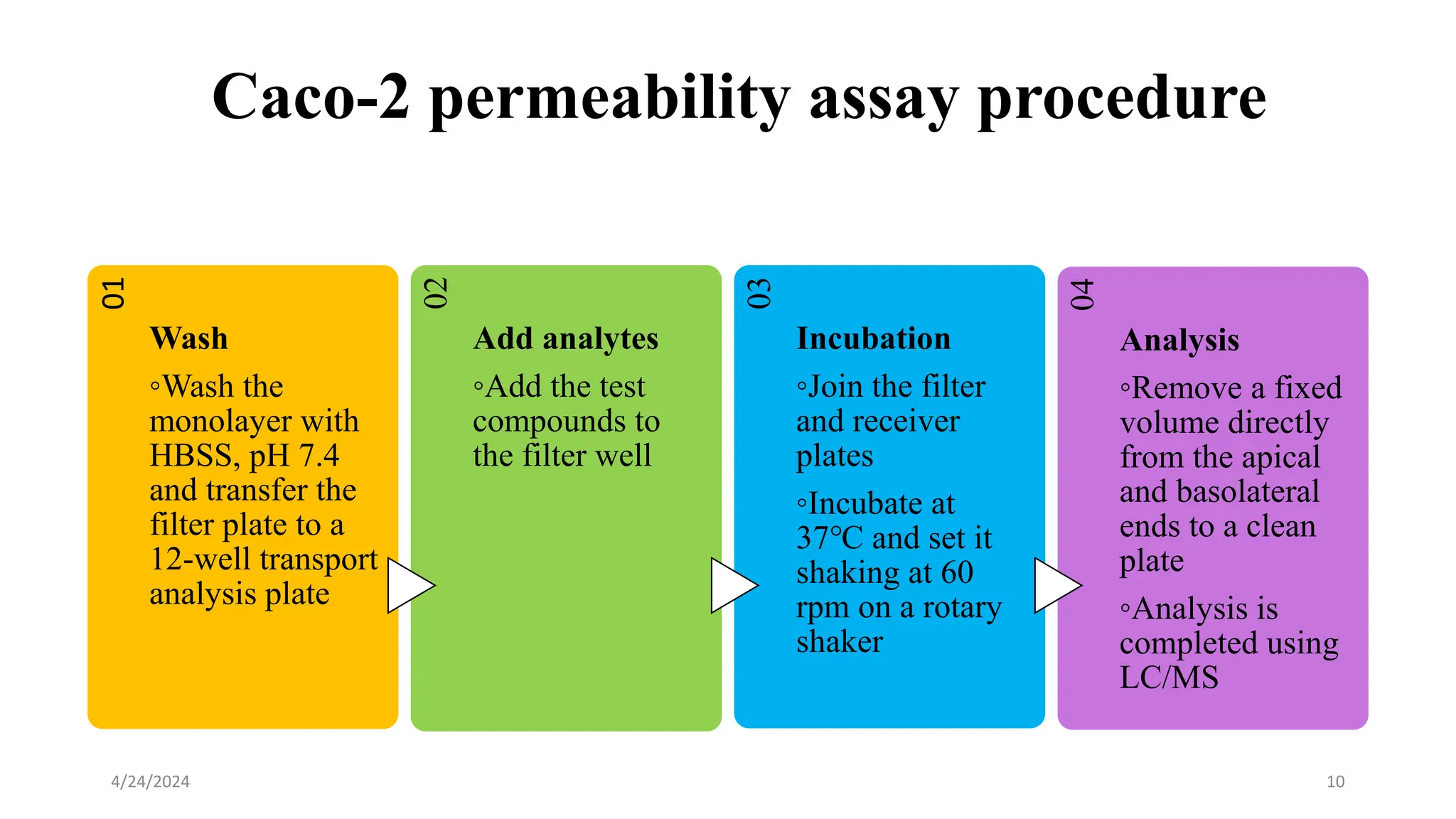
The document discusses the CACO-2 cell permeability assay, which is used to evaluate drug absorption through the human intestine, focusing on factors affecting intestinal absorption such as dissolution rate, solubility, and permeability mechanisms. It explains the characteristics of CACO-2 cells, their differentiation into enterocytes, and the methods for permeability assessment including trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement. The document also outlines the procedure for performing the permeability assay, analyzing results, and interpreting permeability values based on comparison with standard compounds.


![Apparent permeability, Papp(cm/s) & Efflux Ratio
Papp =
𝒅𝑸
𝒅𝒕
×
𝟏
A.C0
Permeability
rate over time
Area of caco-2
covered filter
Initial concentration in
donor compartment
Efflux ratio =
Papp [B → A]
Papp [A → B]
4/24/2024 11
Papp values of < 1-2 × 10−6 cm/ s : low
permeability (0−20% human fraction
absorbed.
Papp values of 2−10 × 10−6 cm/s:
moderate permeability (20−80% Fa)
Papp > 10 × 10−6 cm/ s : high
permeability (80−100% Fa)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caco-2cellpermeabilityassay-240424174608-c4817915/75/Caco-2-cell-permeability-assay-for-drug-absorption-11-2048.jpg)
![4/24/2024 12
Although it is acknowledged that the actual permeability values may vary in Caco-2 monolayer permeability
assays, the assay results are most reliably interpreted in comparison to compounds evaluated in the same
assay, relative to standard compounds representing upper (Propanolol) and lower bounds (fluorescein or
mannitol)
Ctd…
Tegan P. Stockdale, Victoria L. Challinor, Reginald P. Lehmann, James
J. De Voss, and Joanne T. Blanchfield
ACS Omega 2019 4 (4), 7658-7666
DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b00496
Papp values decrease with increasing test compound concentration, suggests the involvement of
transporter pathways.
For example, the measurement of Papp values for a test compound may be repeated in the presence of
verapamil (100 µM) [42] or MK-571 (50 µM) [37], which are inhibitors of P-glycoprotein and MRP,
respectively
When a compound has an efflux ratio of greater than 2, it suggests that the compound may be subject to
active efflux.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caco-2cellpermeabilityassay-240424174608-c4817915/75/Caco-2-cell-permeability-assay-for-drug-absorption-12-2048.jpg)