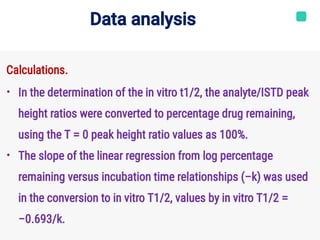
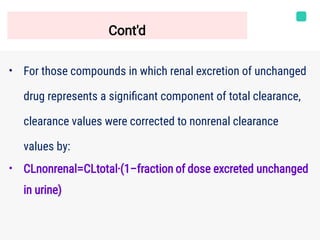
Microsomal stability assays use liver microsomes containing cytochrome P450 enzymes to assess the in vitro metabolic stability of compounds. Liver microsomes are subcellular fragments that contain drug-metabolizing enzymes. The percentage of the parent compound remaining over time is measured in the presence of microsomes and cofactors. This allows the calculation of intrinsic clearance and half-life to investigate Phase I metabolism. Controls are used to characterize specific cytochrome P450 isozymes. The amount of parent compound is quantified by HPLC-MS/MS to determine metabolic stability.