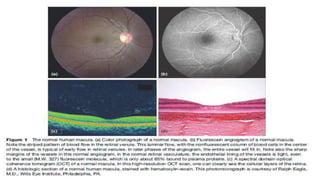
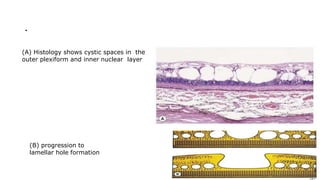
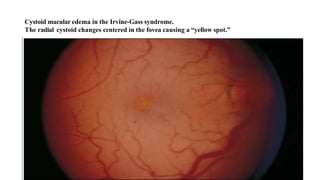
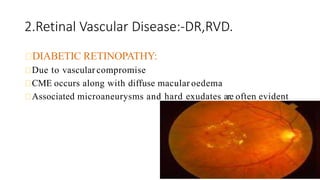
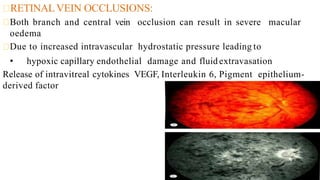
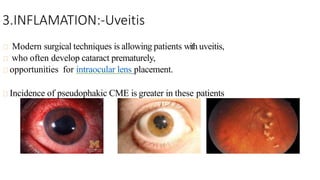
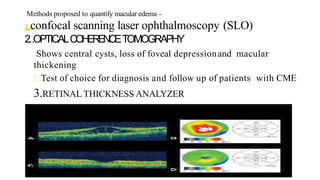
Cystoid macular edema (CME) results from fluid accumulation in the retina's outer plexiform and inner nuclear layers, forming cyst-like spaces. It can be caused by breakdown of the inner and outer blood-retinal barriers or release of inflammatory mediators. CME is commonly seen after cataract surgery or in diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusions. Treatment involves medications like NSAIDs and corticosteroids administered topically, through injections, or intravitreally. For refractory cases, surgical options like vitrectomy may be considered. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and vascular permeability through various pharmacological and surgical means.