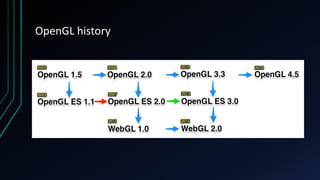
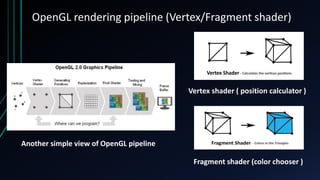
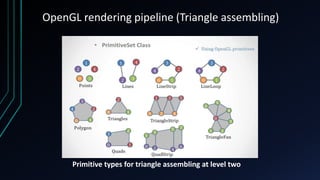
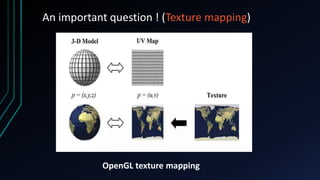
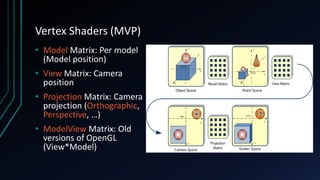
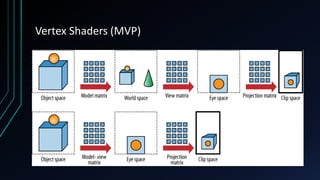
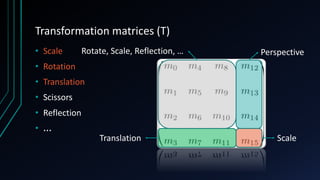
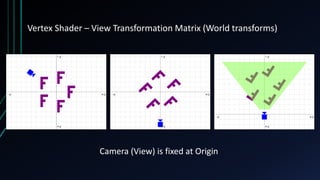
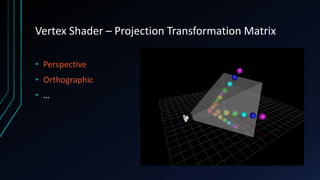
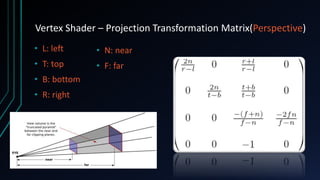
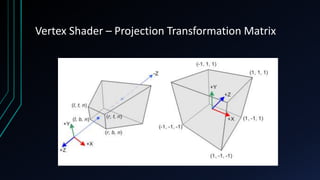
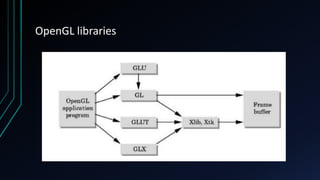
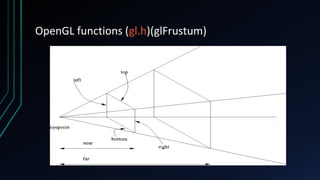
OpenGL is a cross-language, cross-platform API for rendering 2D and 3D graphics via hardware acceleration. It uses shaders and programmable pipelines to process vertices and fragments. The rendering pipeline involves transforming vertices, assembling triangles, rasterization, applying textures, testing fragments, and writing pixels to the framebuffer. Key concepts include transformation matrices, lighting, and the vertex and fragment shaders that operate on data at each pipeline stage.