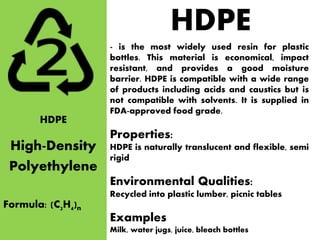
This document discusses the resin identification coding system used internationally to identify different types of plastic polymers. It provides details on 7 common plastic codes:
1) PETE (polyethylene terephthalate) used for water/soda bottles and fibers;
2) HDPE (high density polyethylene) for milk jugs and detergent bottles;
3) PVC (polyvinyl chloride) for pipes, flooring, and furniture;
4) LDPE (low density polyethylene) for bags and food packaging;
5) PP (polypropylene) for yogurt containers and bottle caps;
6) PS (polystyrene) for disposable food packaging and cups;
7