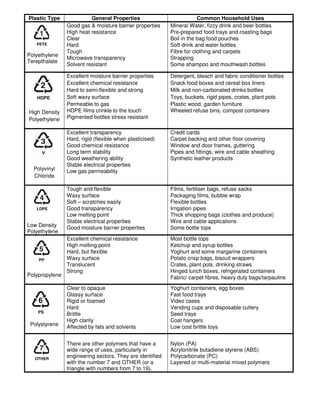
The Society of the Plastics Industry established a classification system using code numbers to identify different types of plastics. This system allows consumers and recyclers to understand what kind of plastic they are dealing with. The codes represent the following types of plastics: PETE (code 1) used for water and soda bottles; HDPE (code 2) used for milk jugs and shampoo bottles; PVC (code 3) used for pipes; LDPE (code 4) used for dry cleaning bags and squeeze bottles; PP (code 5) used for yogurt containers and bottle caps; PS (code 6) used for disposable cups and plastic cutlery; and code 7 for other plastics like polycarbon