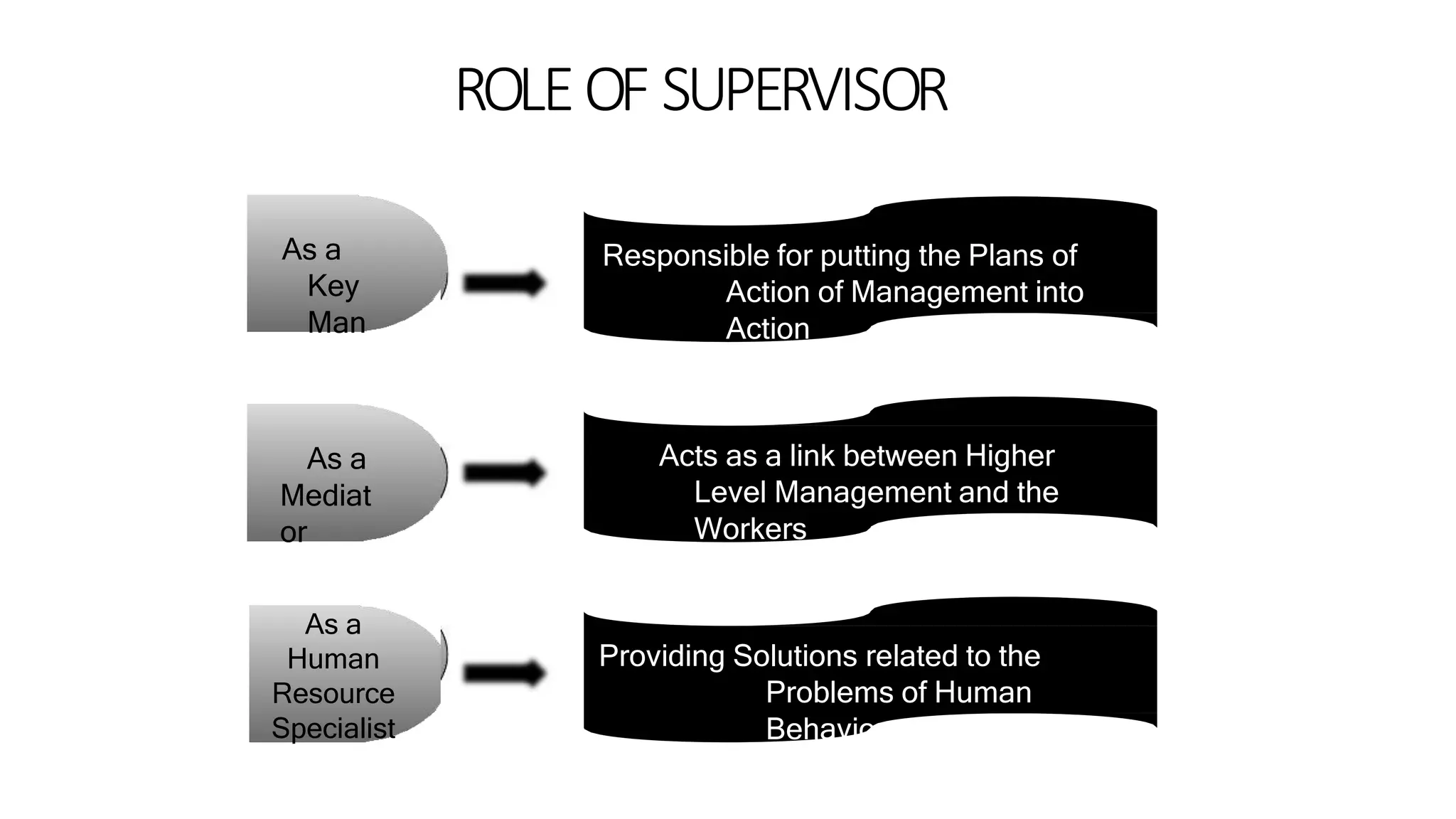
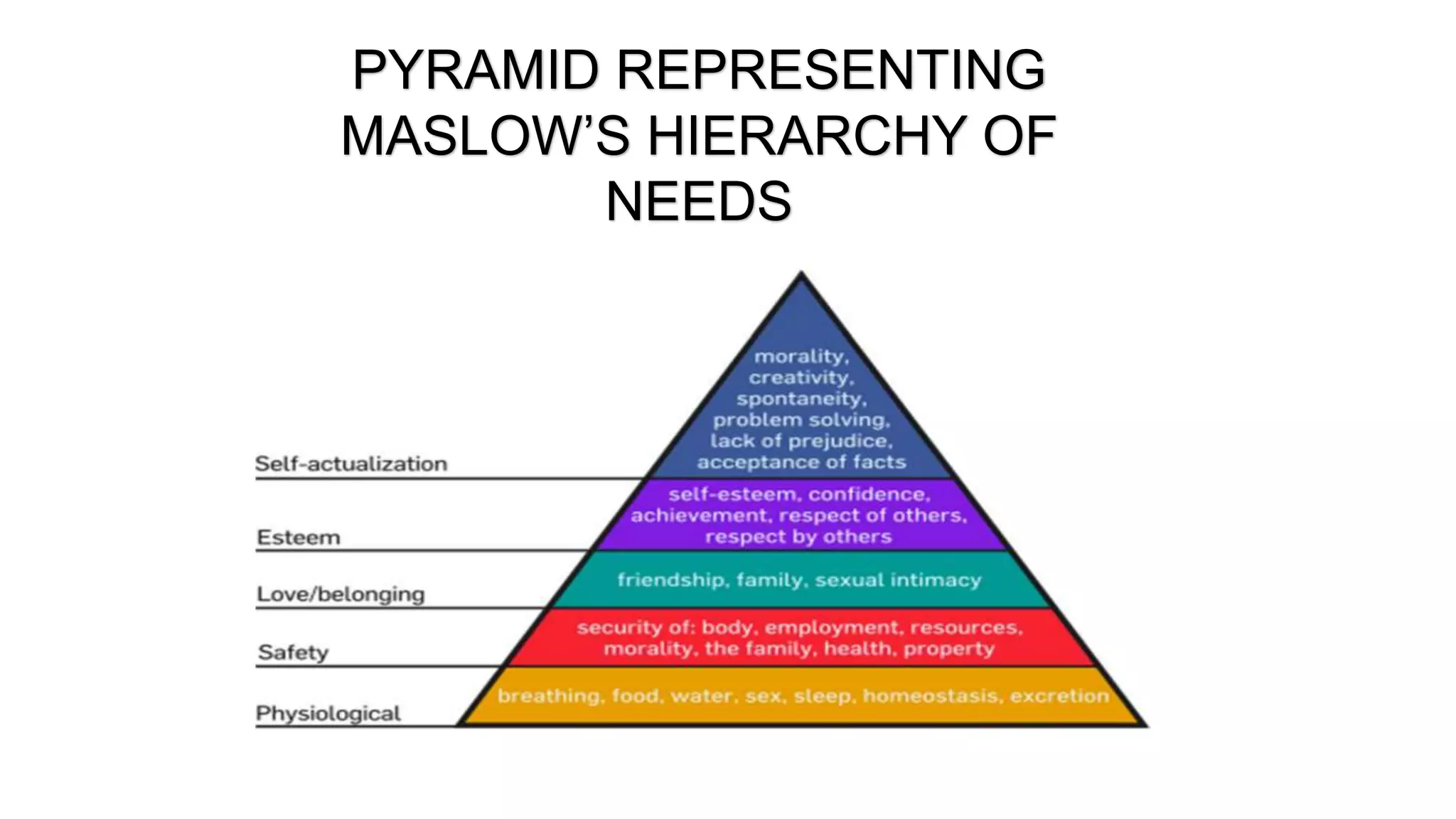
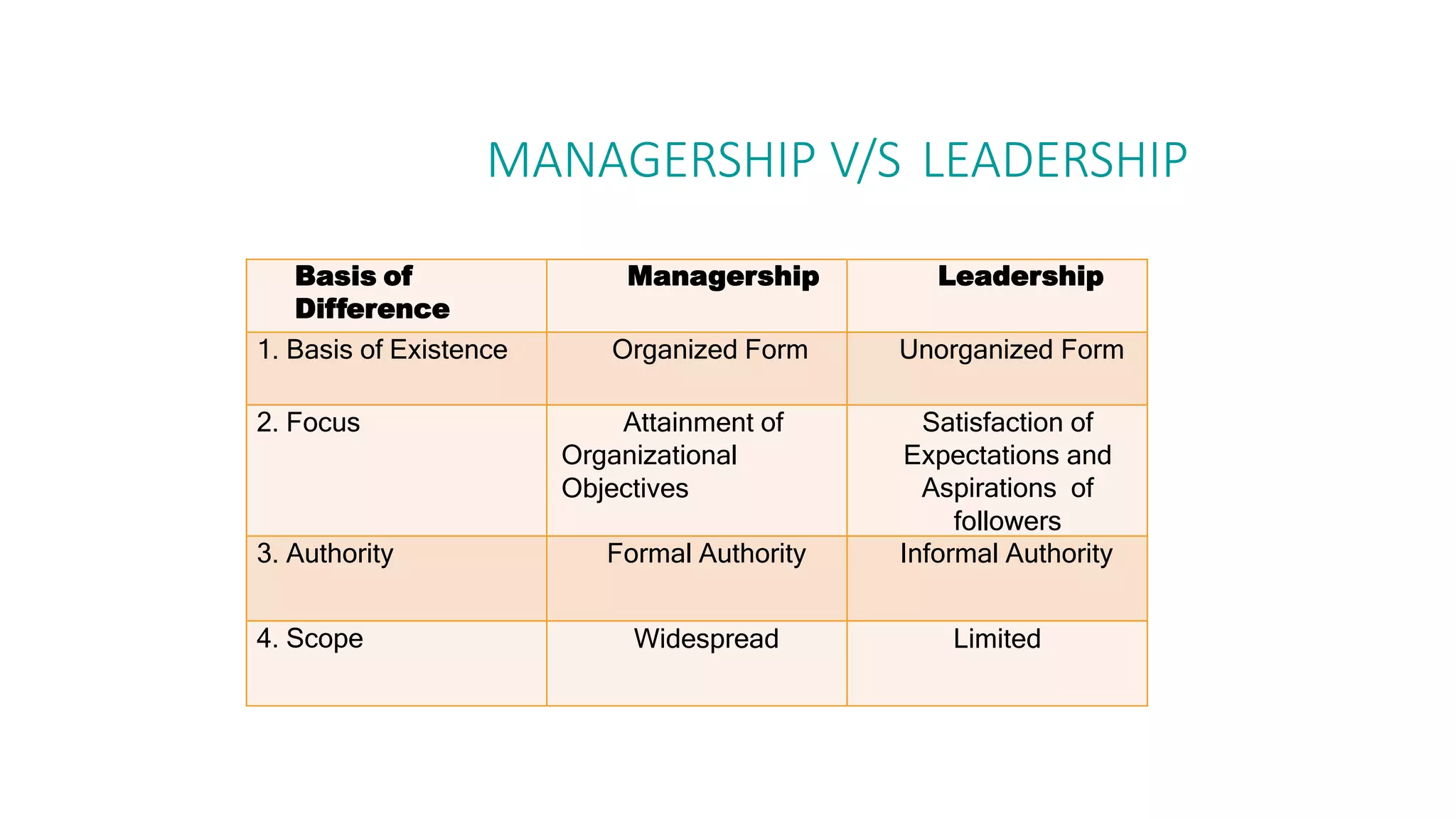
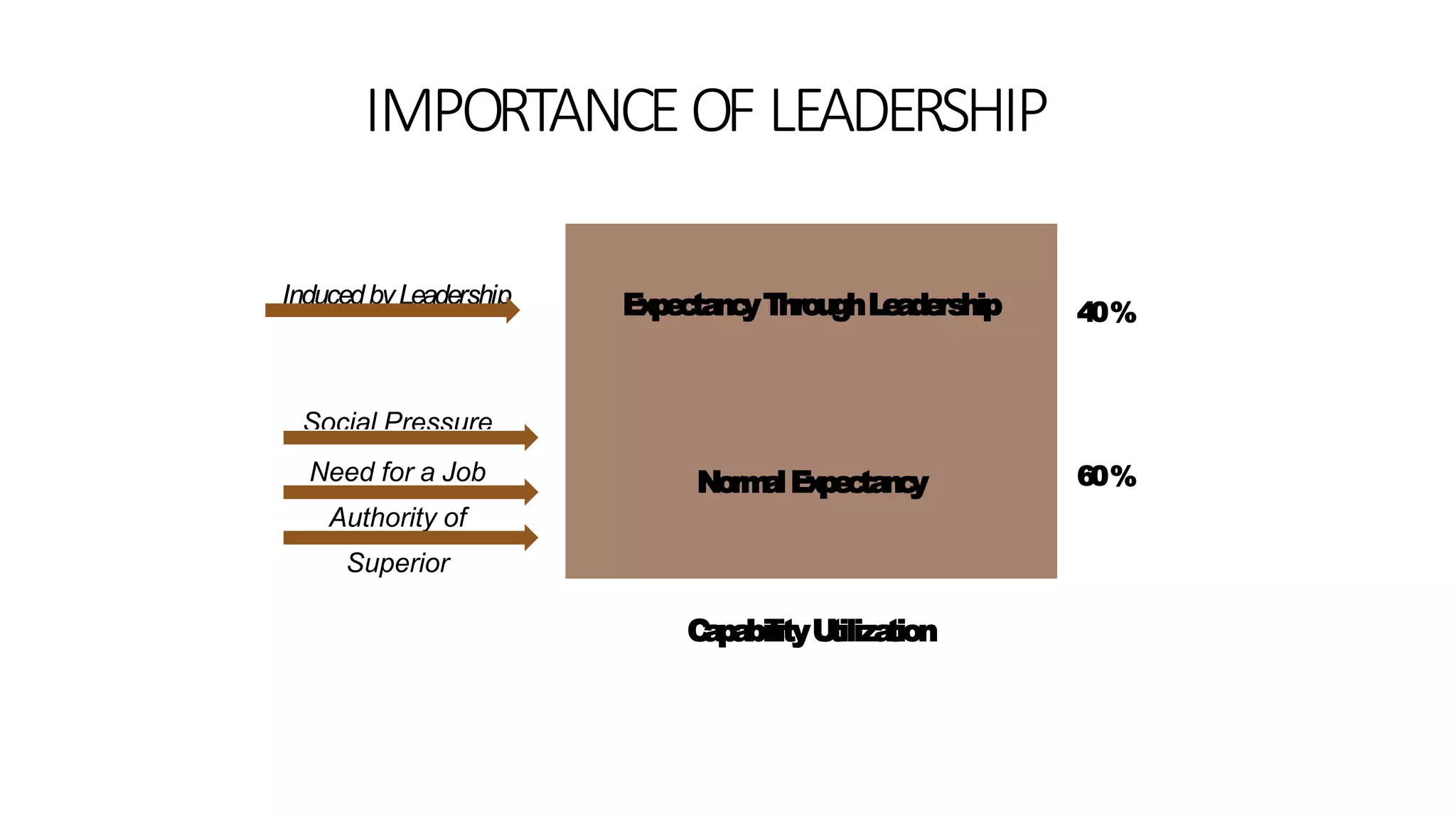
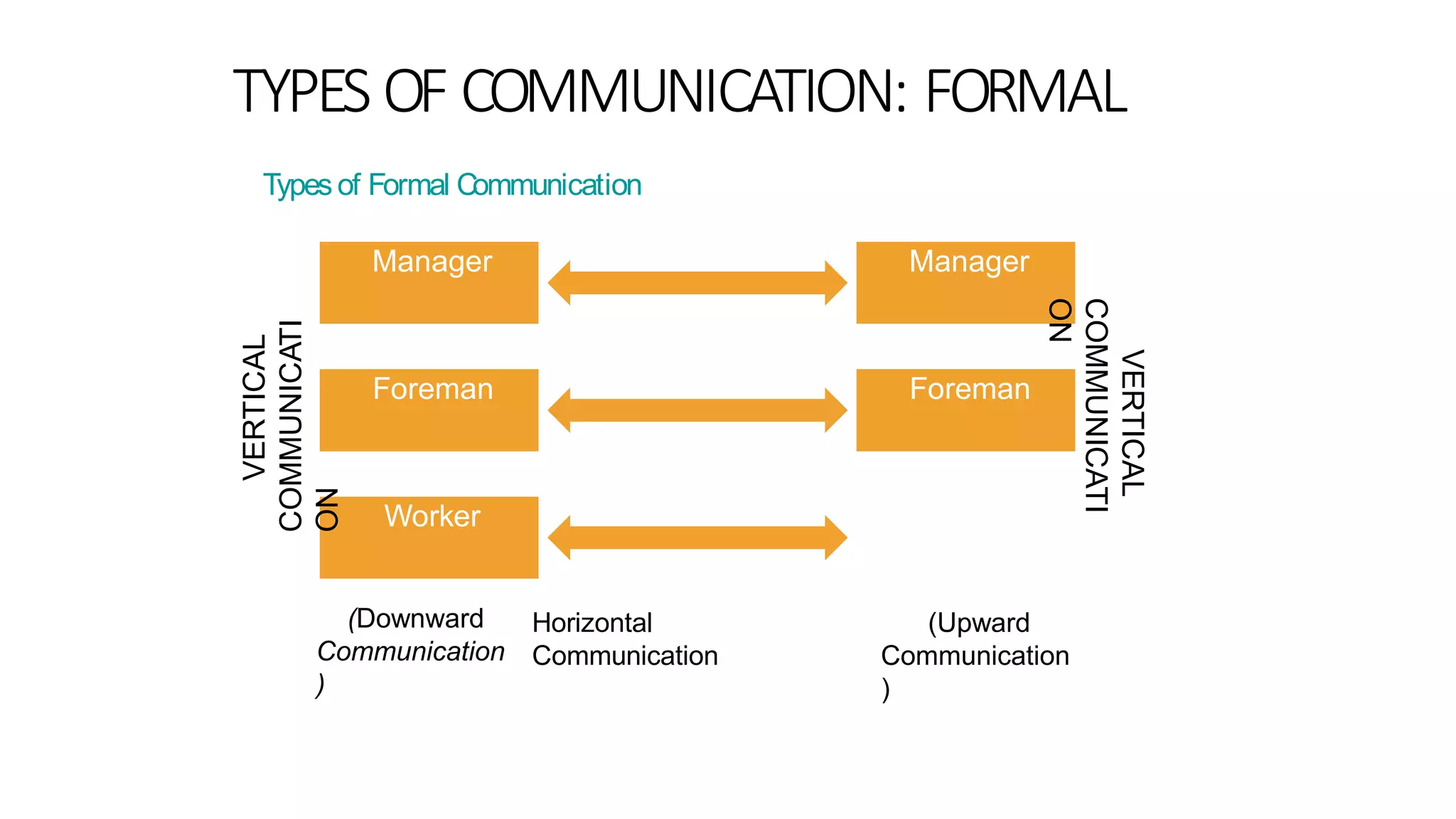
The document discusses the key elements of directing including supervision, motivation, leadership, and communication. It describes concepts like Maslow's hierarchy of needs and different leadership styles such as autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. Barriers to effective communication are also covered along with ways to overcome them to ensure proper information flow within an organization.