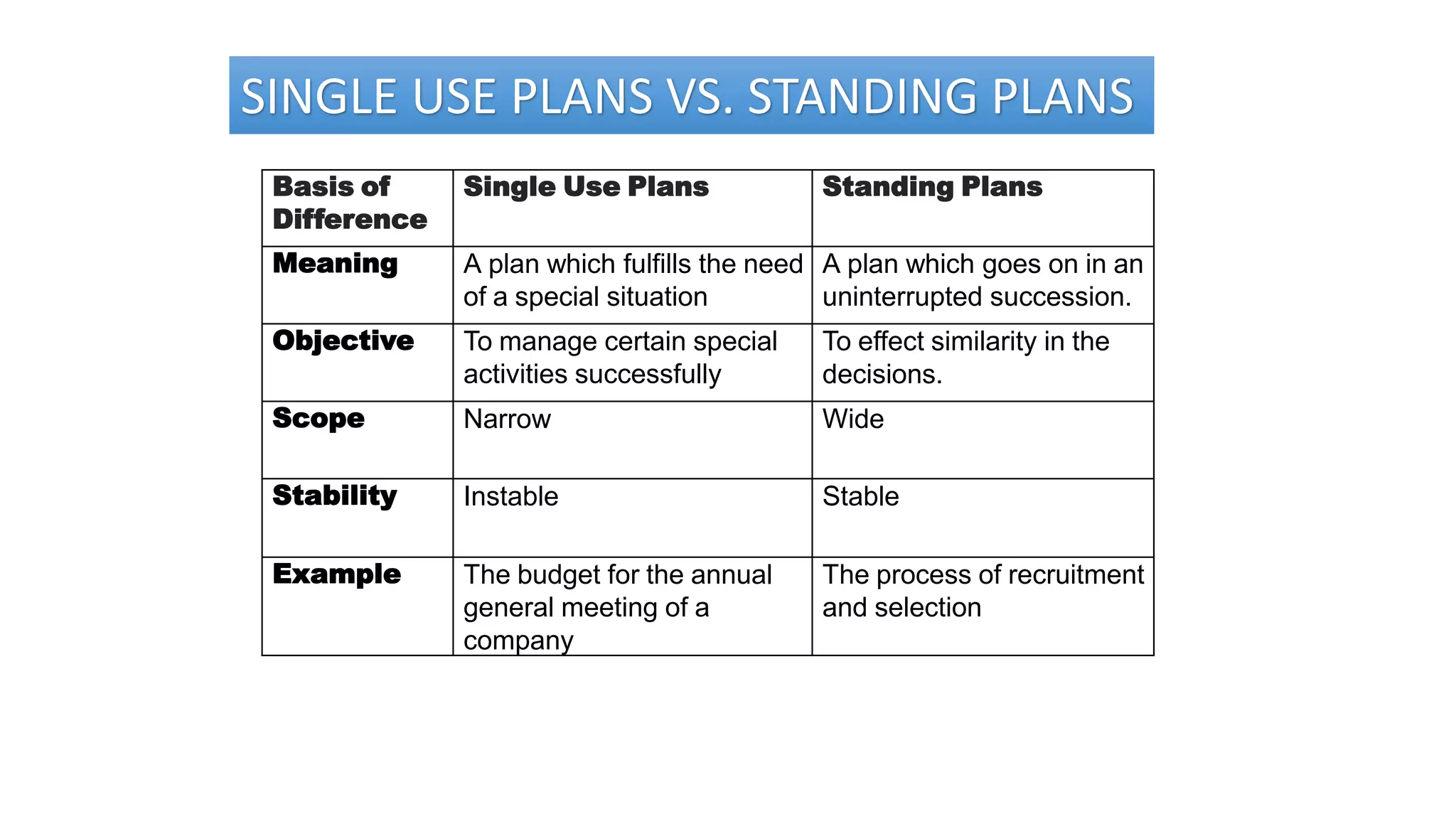
This document discusses planning and the planning process. It defines planning as thinking ahead about what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who will do it. The planning process involves setting objectives, developing premises, identifying alternative courses of action, evaluating alternatives, selecting an alternative, implementing the plan, and follow up action. There are two main types of plans: standing plans that provide continuous guidance and are used repeatedly, and single use plans that provide guidance for specific non-recurring problems. Examples of different types of plans include objectives, strategies, policies, procedures, methods, rules, budgets, and programs.