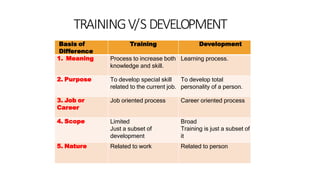
Staffing involves recruiting, selecting, training and developing employees. It is an important part of human resource management. The key aspects of staffing include recruitment through various sources like promotions, transfers, advertisements. Selection involves screening applicants through tests and interviews. Training helps improve employee skills and may be on-the-job or off-the-job. It benefits both the organization and employees. Staffing is essential for organizations to obtain competent staff, improve performance and ensure continuous growth.