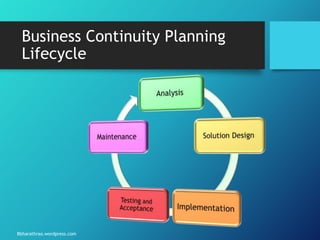
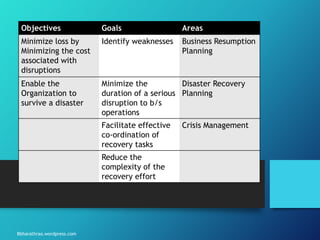
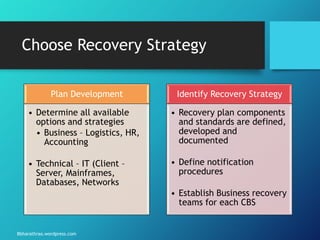
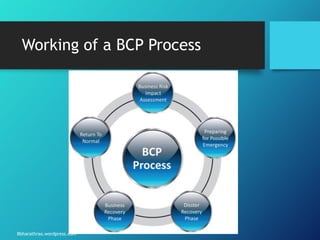
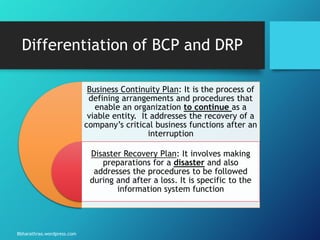
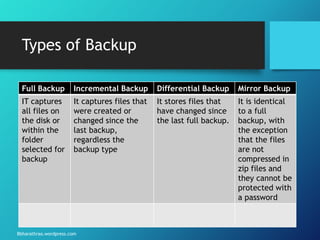
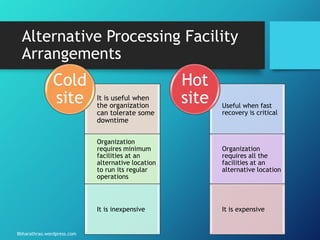
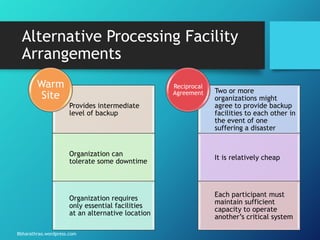
The document outlines the processes and strategies involved in business continuity planning (BCP) and disaster recovery planning (DRP), emphasizing the importance of having a practical plan to restore operations following a disaster. It details the lifecycle of BCP/DRP, including risk assessment, recovery strategies, types of plans, and the significance of regular testing and updates. Additionally, it discusses the various types of backup options and alternative processing facilities that organizations can utilize to ensure operational resilience.