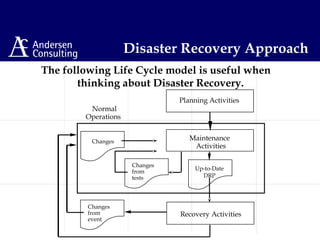
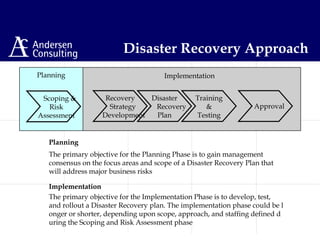
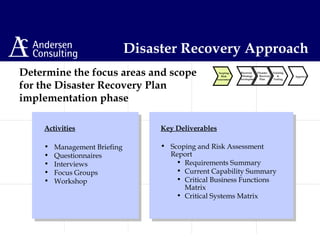
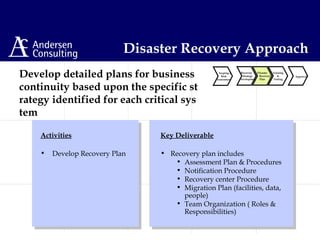
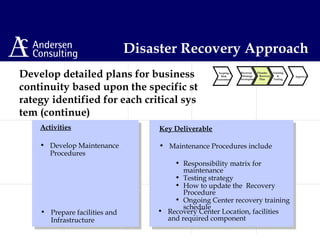
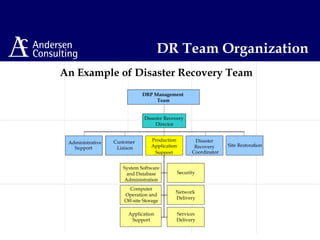
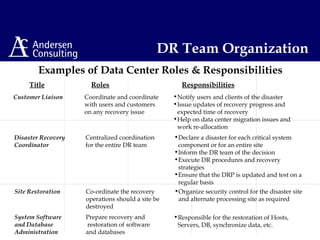
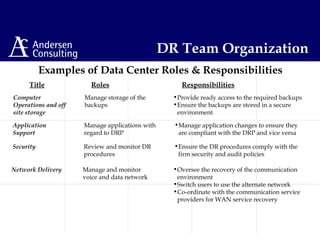
This document discusses disaster management and disaster recovery planning. It begins with defining what constitutes a disaster and provides examples of past disasters. It then discusses what a disaster recovery plan is and the key components of developing a plan, including assessing risks, developing recovery strategies, creating detailed recovery plans, and testing plans through training and exercises. The overall approach involves scoping, planning, implementing, and maintaining a disaster recovery plan on an ongoing basis.