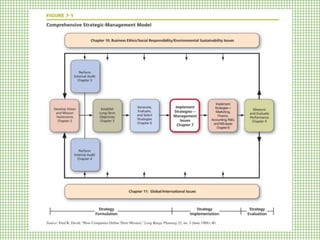
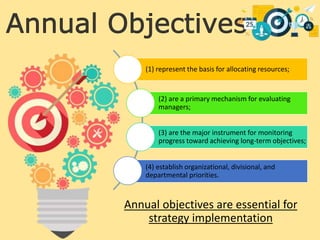
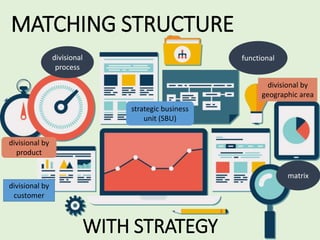
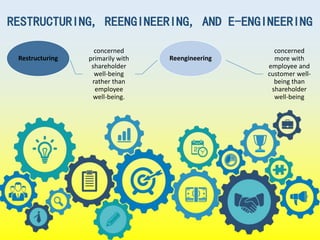
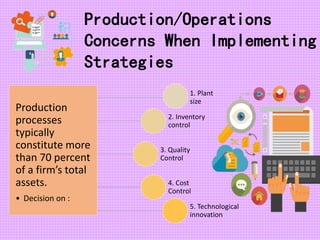
This chapter discusses strategy implementation and contrasts it with strategy formulation. Strategy implementation requires operational coordination across many individuals, focusing on efficiency. It involves altering structures, processes, and incentives to support new strategies. Annual objectives are important for allocating resources, evaluating managers, and monitoring progress. Organizational structure must match strategy to enable implementation. Restructuring changes ownership priorities while reengineering changes processes to benefit employees and customers. Performance pay can be linked to strategies through bonus and profit-sharing systems. Managing resistance to change is key through education, self-interest appeals, or forcing change. Culture shapes implementation and must be modified to support new strategies. Production concerns include decisions around assets, processes, quality, and innovation.