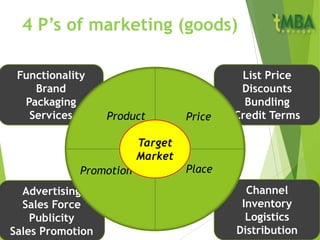
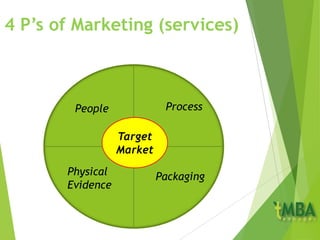
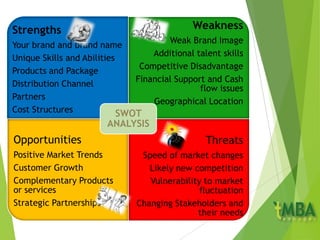
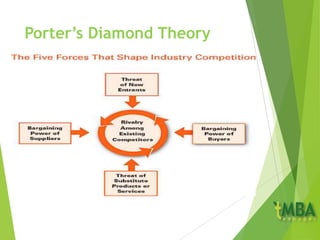
The document outlines key aspects of marketing planning covered in Chapter 2. It discusses the components of a marketing plan including objectives, strategic plans, specific actions, and budgets. Objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Timely). The marketing mix of the 4 P's (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) is explained for both goods and services. Ethics in marketing and conducting marketing audits and SWOT analyses are also covered.