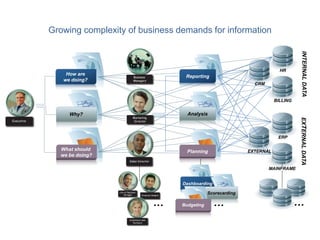
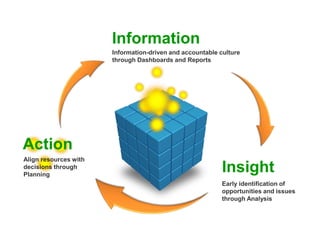
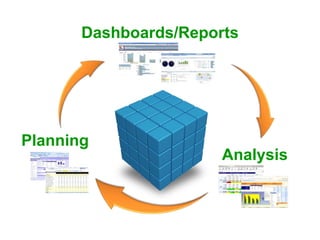
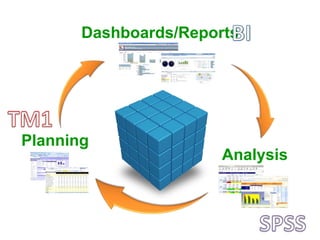
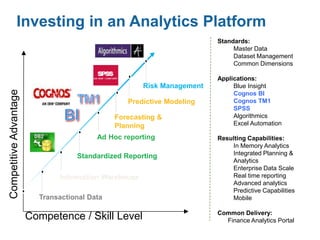
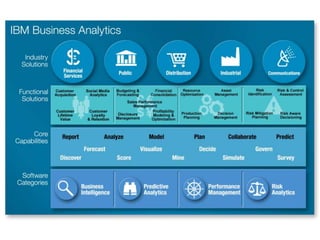
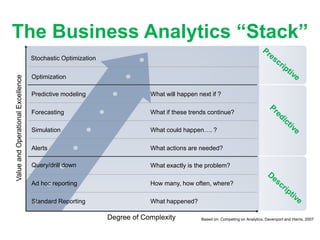
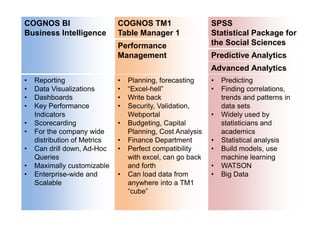
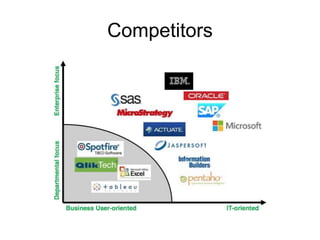
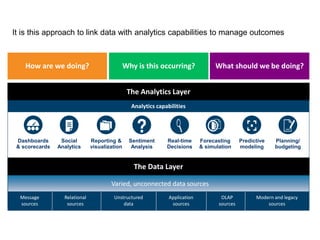
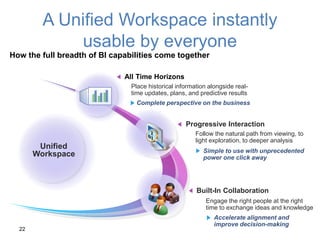
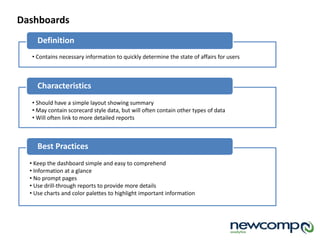
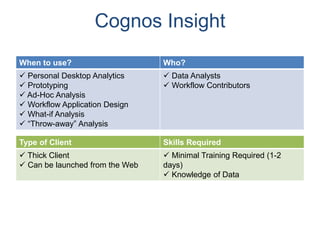
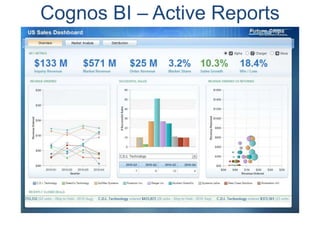
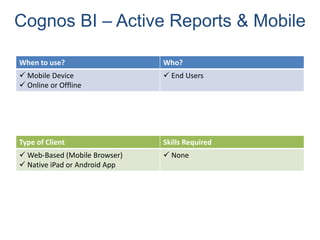
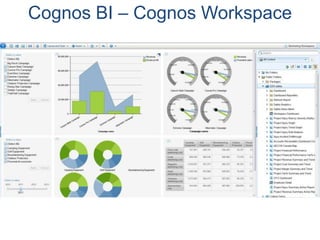
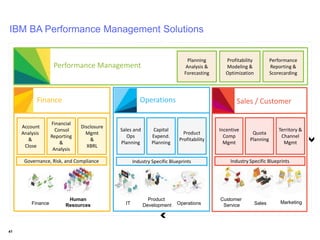
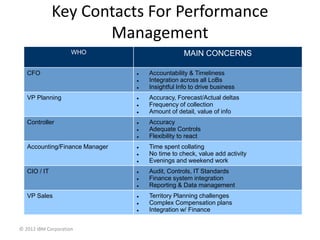
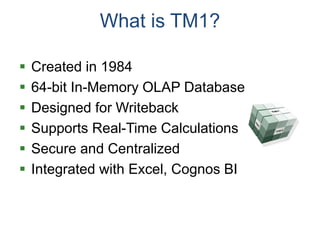
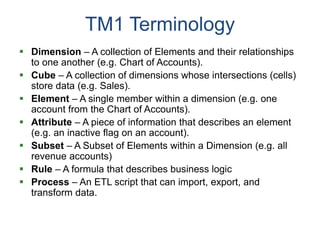
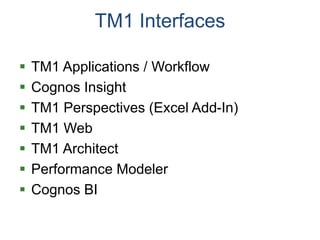
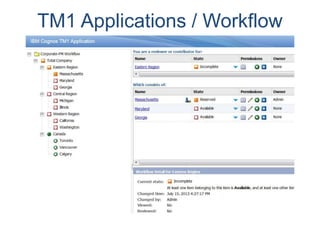
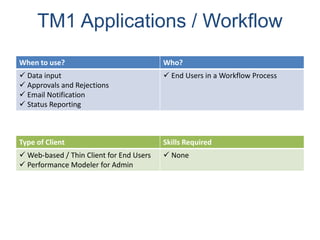
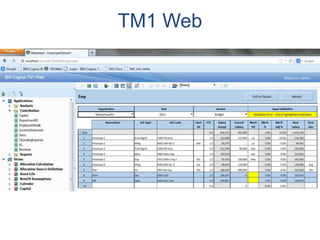
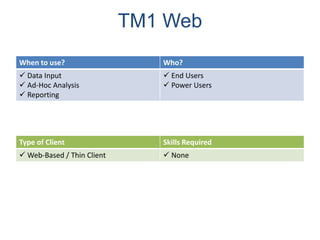
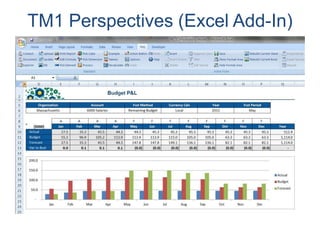
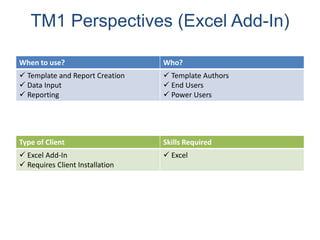
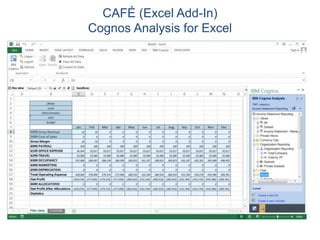
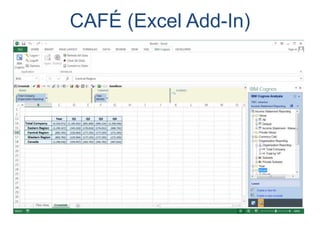
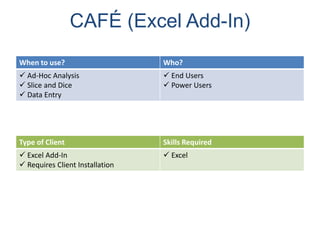
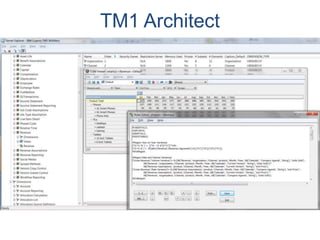
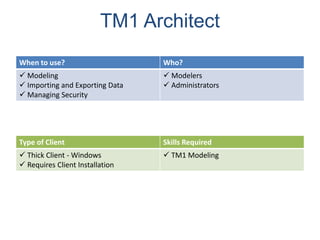
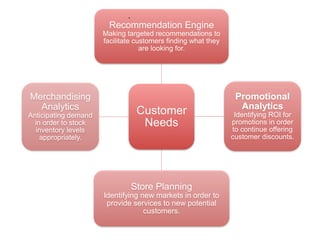
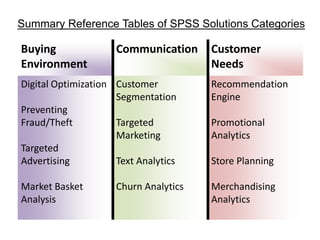
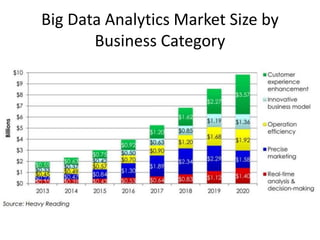
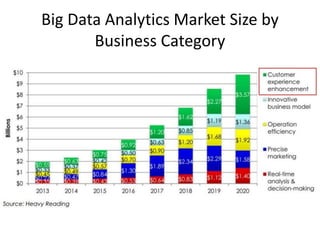
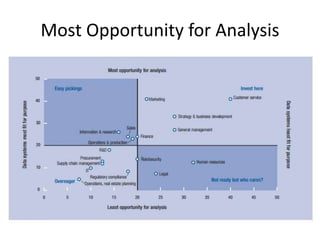
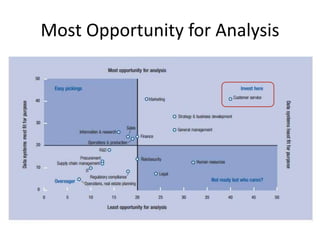
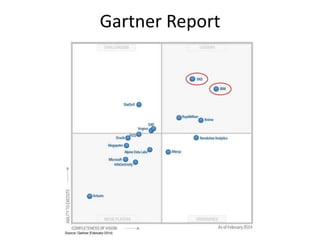
IBM offers a business analytics portfolio including Cognos BI, Cognos TM1, and SPSS to provide capabilities across reporting, planning, analysis, and predictive analytics. The suite integrates various data sources and allows different levels of analytics from basic reporting and dashboards to more advanced predictive modeling and optimization. It provides a unified workspace and promotes collaboration.