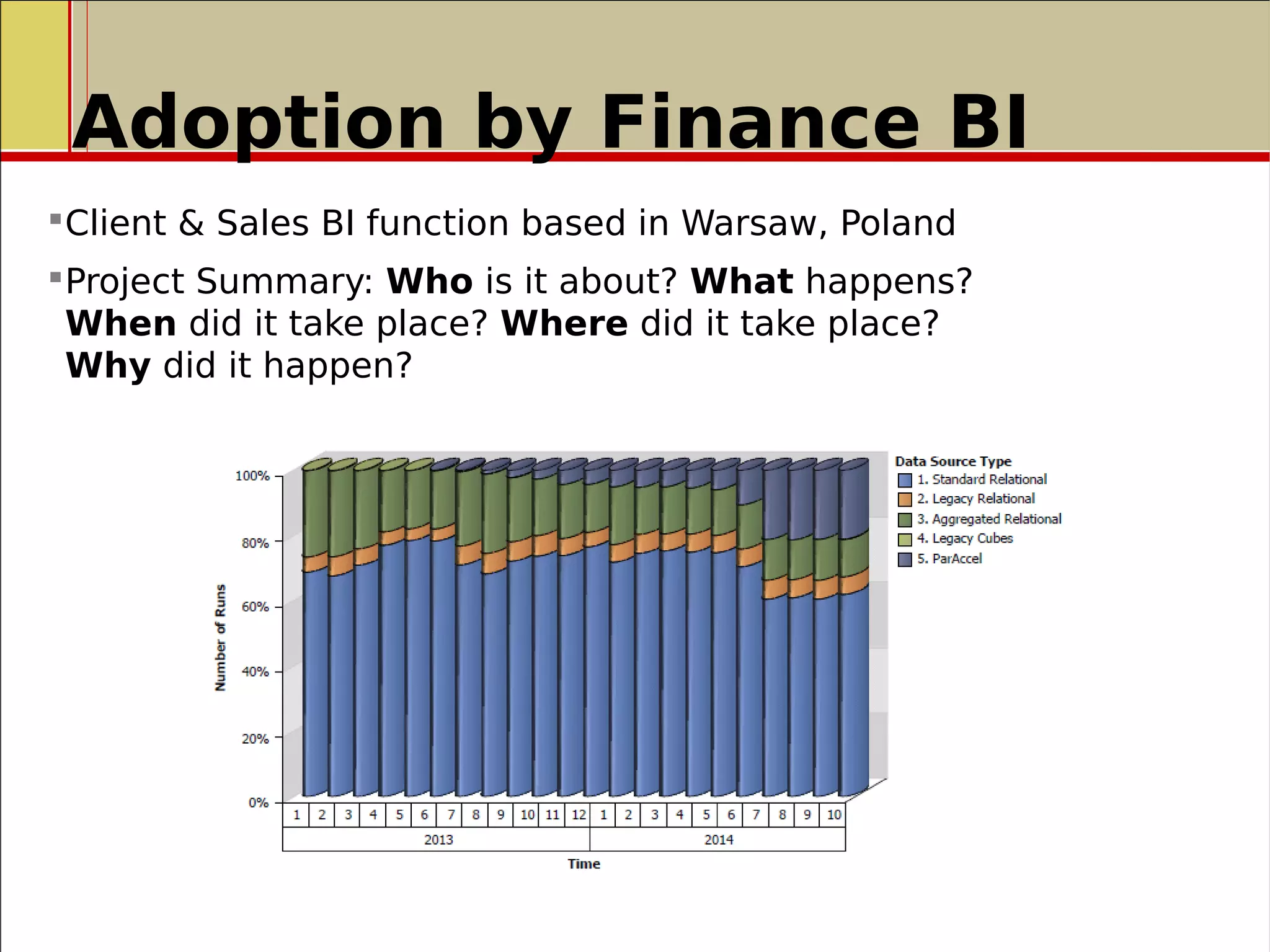
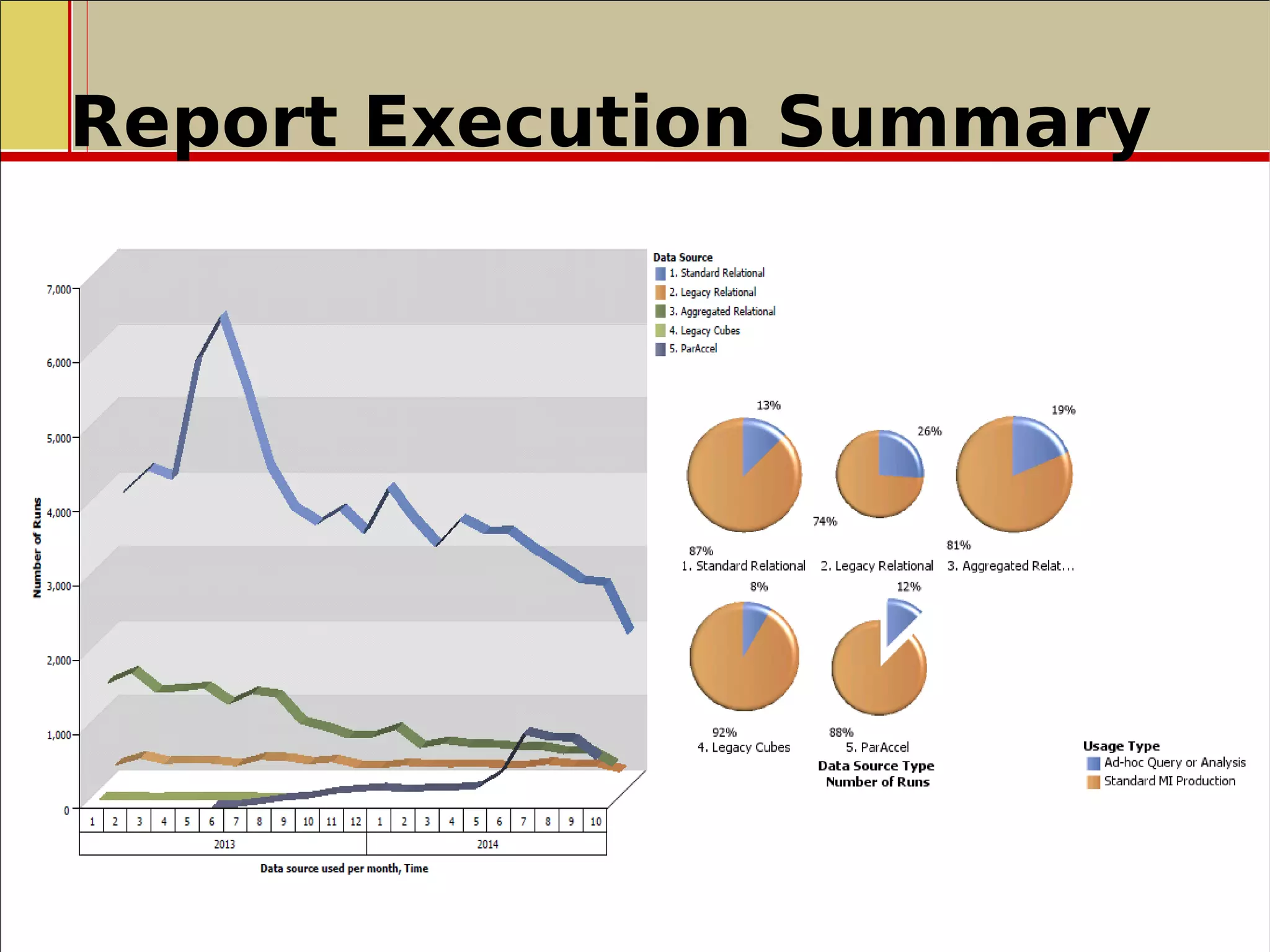
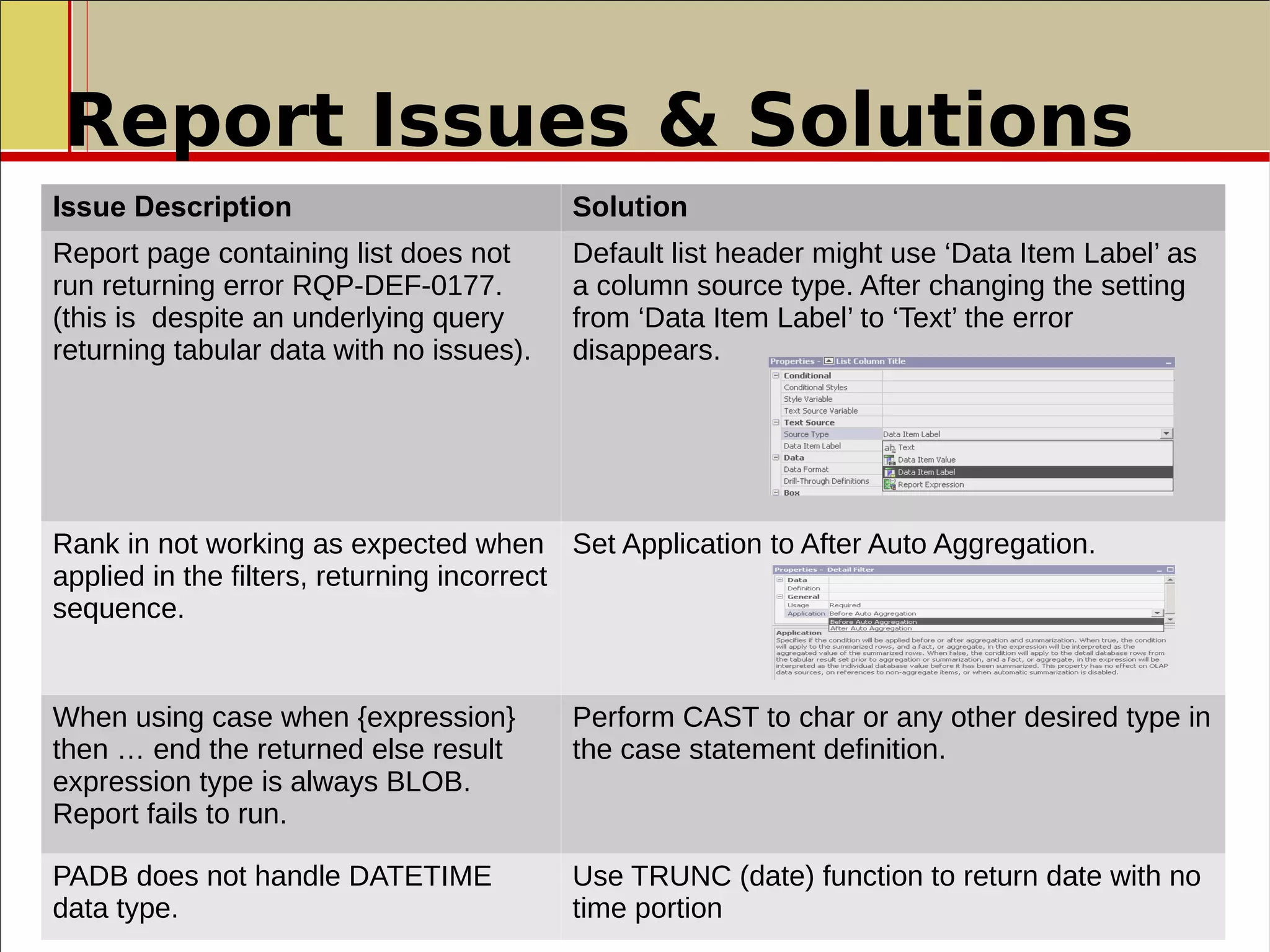
The document outlines a presentation on the implementation of a high-performance business intelligence solution using IBM Cognos and the Paraccel analytic database. It discusses key business intelligence concepts, the benefits of advanced analytics, and the successful rollout of the technology in a global investment banking division, which significantly improved reporting execution times and reduced data latency. The presentation concludes with recommendations for further enhancements and optimizations following the implementation.




![Concepts - DWH System
Real-Time
Massively Parallel Processing
(MPP):
Shared Nothing vs Shared
Everything
Near-linear Scalability
Big Data:
“Big data is like teenage sex:
everyone talks about it,
nobody really knows how to do
it, everyone thinks everyone
else is doing it, so everyone
claims they are doing it…”
–Dan Ariely
MPP OLAP
Database
Typical OLTP
Database
Large volumes of
data (TB to PB)
Smaller volumes of
data (GB to TB)
Low number of
power database
users
High number of
concurrent light
users
Complex analytic
queries
Optimized of single
row access
Low level of data
granularity (Facts)
High use of tuning
structures
Decision support,
and what if
scenarios
Transaction
processing
and data integrity
Bulk data loading
(TB / day is typical)
Low volume data
loading
References: Press, G. (2013, June 03). [Text]. Retrieved from
http://whatsthebigdata.com/2013/06/03/big-data-quotes/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-6-2048.jpg)
![BI Platforms
Business Intelligence (BI) and
analytics systems are applications
and technologies for gathering,
storing, analyzing, and accessing
information for better business
decision making to gain
competitive advantage.
What is IBM Cognos BI?
What is ParAccel Analytic Database
(PADB)?
Strong hints:
- on my employer's name
- on why we actually should it PADB
- Data sheet Data sheet of
a new product References: Henschen, D. (2014, February 26). Gartner BI Magic Quadrant: Winners & Losers [Image
file]. Retrieved from http://www.informationweek.com/big-data/big-data-analytics/gartner-bi-magic-
quadrant-winners-and-losers/d/d-id/1114013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-7-2048.jpg)
![References: Manoria, V. (2012, May 3). IBM Cognos 10 BI: Components & User Interfaces
[Image files]. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/blogs/ibm-bi-
capabilities/entry/ibm_cognos_10_bi_components_user_interfaces1?lang=en
IBM Cognos BI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-8-2048.jpg)
![Actian Analytics Database
Created by ParAccel, and known as ParAccel
Analytic DataBase (PADB), now re-branded
to Actian Analytics Database - Matrix
Parallel processing database management
system designed for high performance
advanced analytics for business
intelligence:
I/O: Columnar & Compressed
CPU: Fully Compiled Queries
Interconnect: MPP Grid Protocol for inter-
node communications.
Core Components
Leader node
Compute node
Interconnect
SAN Integration
Runs on Red Hat or Cent OS! References: Anderson, D. (2012, July 24). Column Oriented Database Technologies [Image files].
Retrieved from http://www.dbbest.com/blog/column-oriented-database-technologies/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-9-2048.jpg)
![ Adaptive Compression (~4x) and no
performance structures:
Using columnar storage, each block holds
column field values for more records then in
row-based storage. As a result reading the
same number of column fields for the same
number of records requires proportionally
less I/O operations
Blocks hold the same data type, so
compression can can be selected based on
the column type of data stored in a block
(mostly, delta, bytedict, runlength, text)
High-performance MPP optimizer (Omne)
Cost-based, Columnar aware
●
Founded on PostgreSQL Planner/Optimizer
Unlimited Table Join Ability (patented) for
use in complex database schema
referenced by views
View Folding for planning through views,
eliminating unused columns
References: Saama blog (2014, October 20). On Big Data and In-Memory Data Clouds [Image file].
Retrieved from http://www.saama.com/on-big-data-and-in-memory-data-clouds/
Columnar storage vs row-wise database
storage:
Data blocks store column values for
consecutive rows
Data blocks store values for
consecutive rows making up the entire
record
Actian Analytics Database](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-10-2048.jpg)
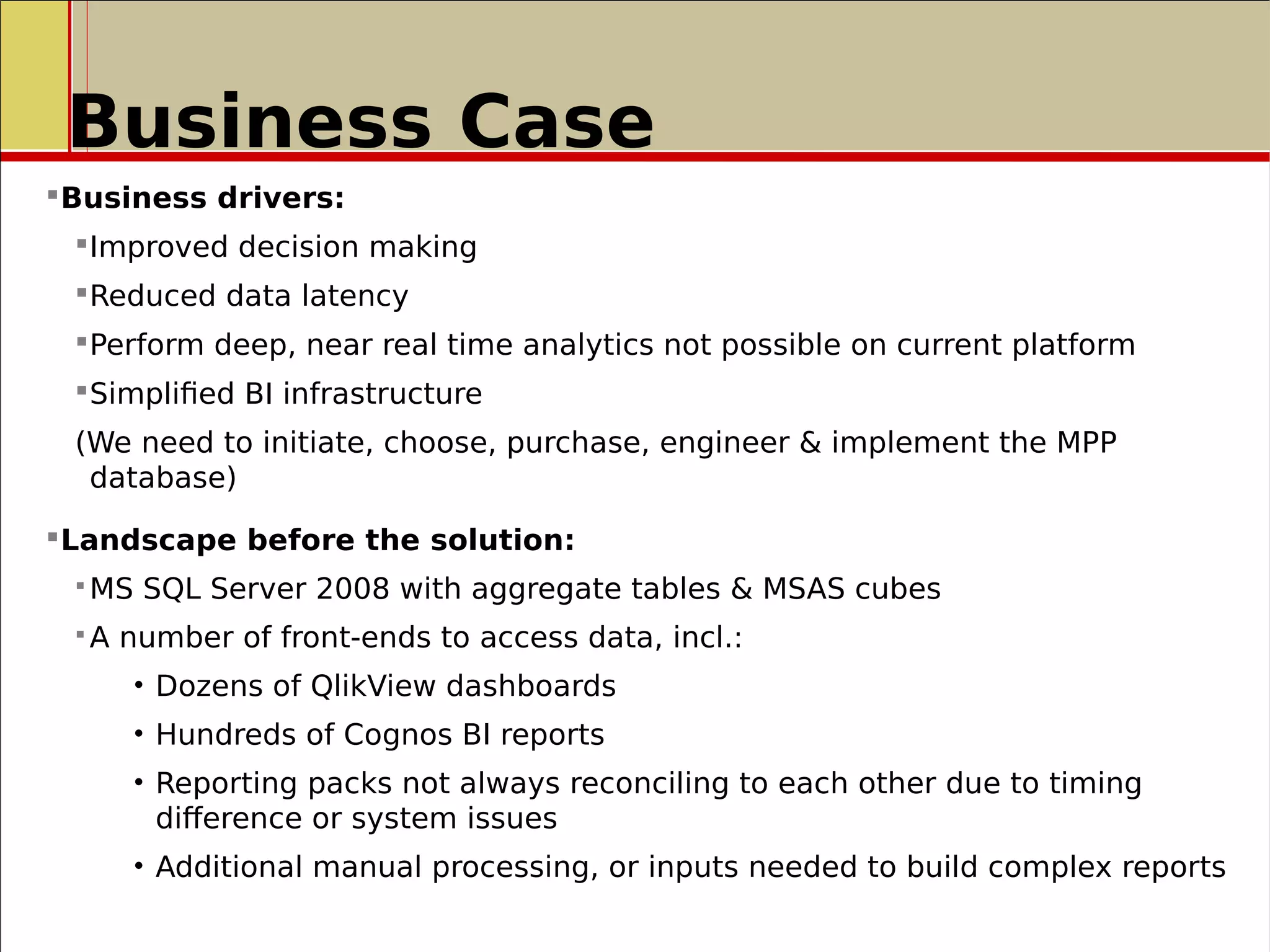
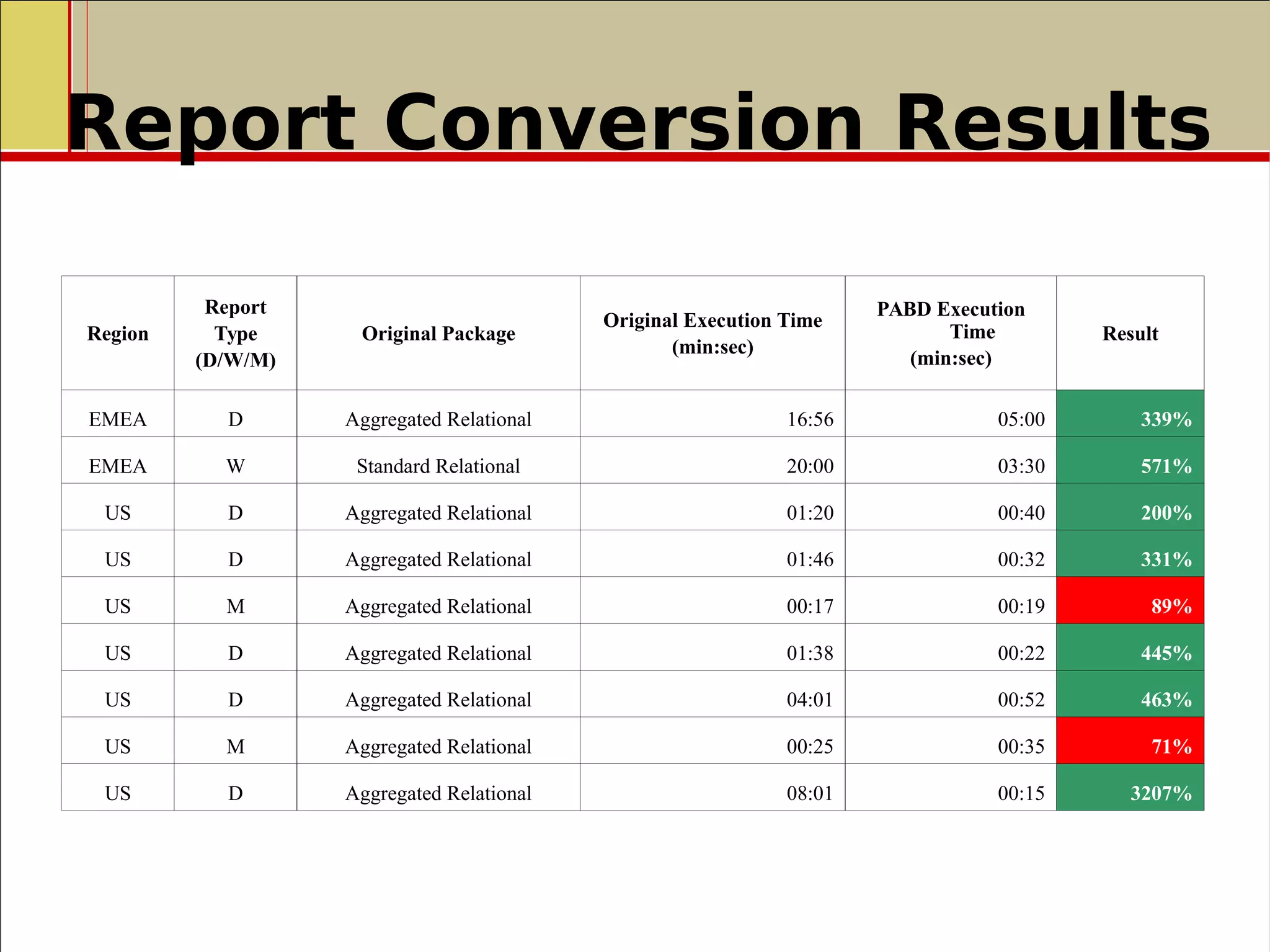
![Front Office Implementation
PoC was done in 2011 and that PADB
was the best fit for the business use
case, winning with Sybase IQ SMP &
PlexQ.
Implementation happened in Q3
2012 and brought:
- Introduction of MPP Database
technology reduced query times
from minutes to sub seconds
- Reduced data processing from T+1
to near real-time
(within 5 minutes from trade
received to available for reporting)
- Introduction of high performance
analytics
New strategic platform delivered to
bank's clients
References: Slicker city blog (2014, June 24). Rogers' technology adoption curve [Image file]. Retrieved
from http://slickercity.net/tag/information-communication-technology/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/high-performancebiwithcognosandpadb-151009231852-lva1-app6891/75/High-Performance-BI-with-Cognos-and-ParAccel-Analytic-Database-12-2048.jpg)