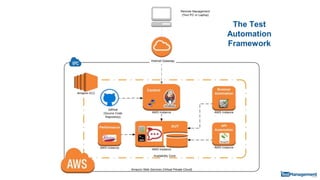
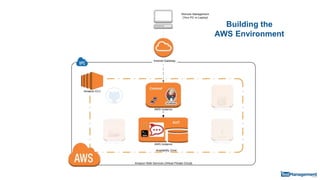
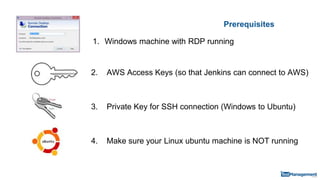
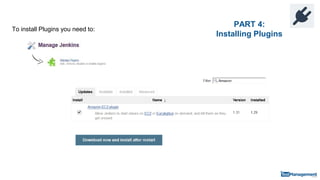
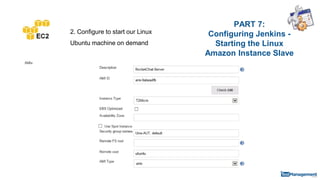
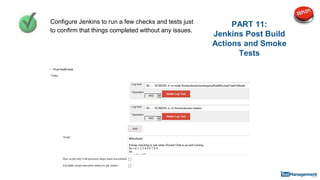
The document is a comprehensive guide on building a test automation framework using Jenkins, detailing installation and configuration processes. It covers essential topics such as integrating Jenkins with AWS, setting up plugins, and running automated tests. The guide also provides instructions for managing Jenkins slave nodes and handling subsequent builds efficiently.