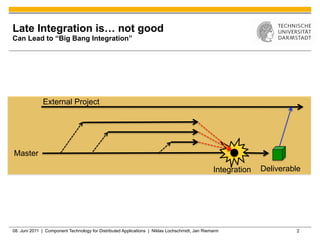
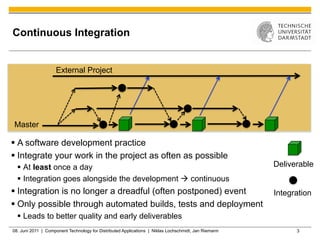
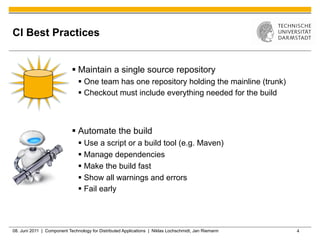
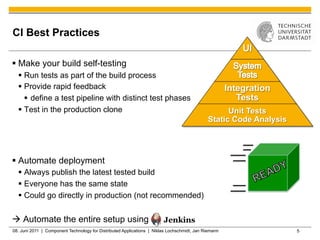
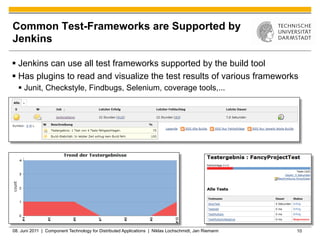
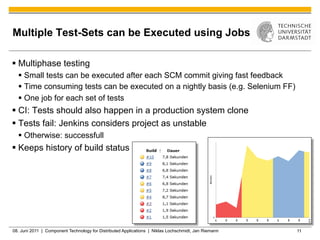
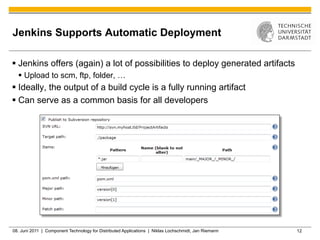
Jenkins is a tool that supports continuous integration by automatically building, testing, and deploying code changes. It integrates code changes frequently, at least daily, to avoid "big bang" integrations. Jenkins runs builds and tests across multiple platforms using slave nodes. It supports various source control systems and build tools and notifies developers of failed builds or tests through email or other plugins.