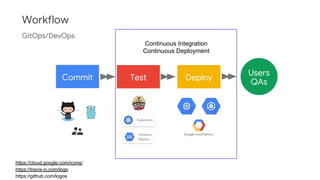
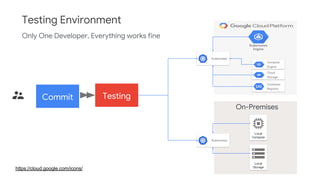
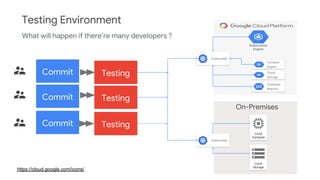
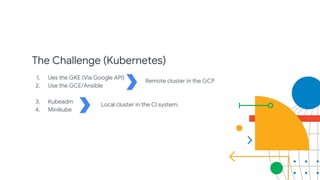
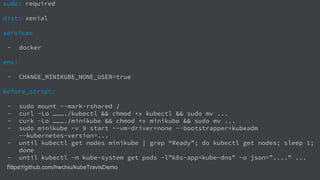
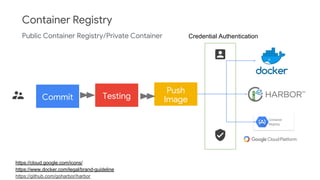
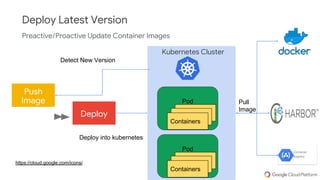
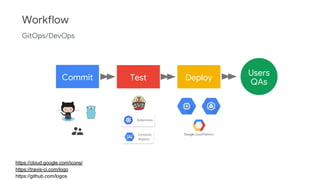
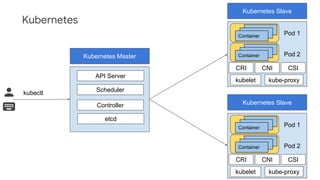
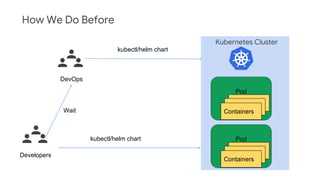
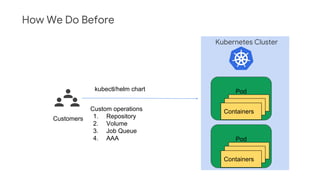
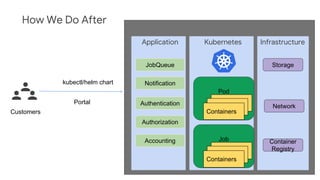
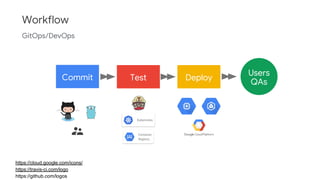
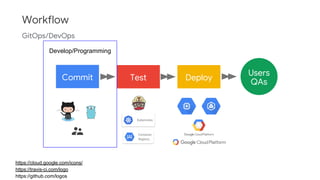
The document discusses Kubernetes as a container-centric management platform that facilitates agile application deployment and microservices orchestration. It outlines the concept of Container as a Service (CaaS), detailing how to manage container lifecycles using Kubernetes, and emphasizes the importance of CI/CD integration for developers. Additionally, the document describes the necessary steps for building a CaaS platform, testing environments, and continuous integration and deployment processes within Kubernetes.





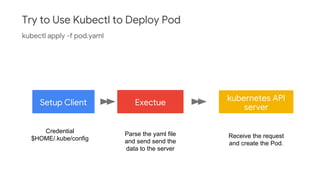

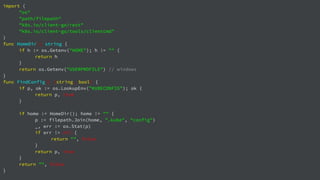
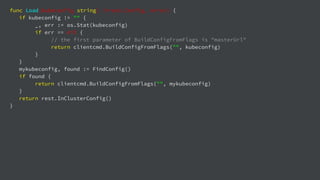
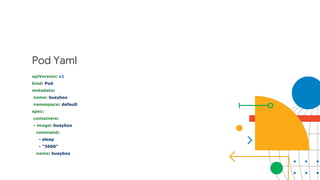
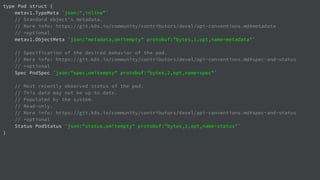
![import (
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/linkernetworks/kubeconfig"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
)
func createPod(clientset *kubernetes.Clientset, name string) error {
_, err := clientset.CoreV1().Pods("default").Create(&corev1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: name,
},
Spec: corev1.PodSpec{
Containers: []corev1.Container{
{
Name: name,
Image: "busybox",
Commands: []string{"sleep",”3600”},
},
},
},
})
return err
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gdgdevfest2018-presentationslidestemplate1-181117073015/85/Build-Your-Own-CaaS-Container-as-a-Service-28-320.jpg)