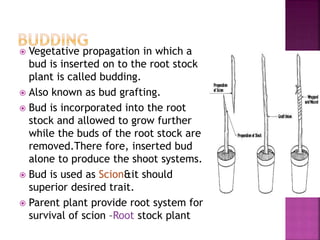
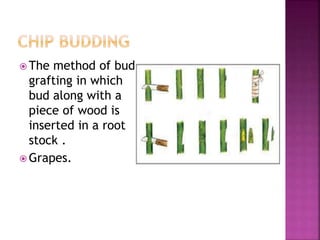
This document discusses various methods of vegetative propagation, specifically grafting. It defines grafting as attaching the shoot of a superior plant to the root stock of an inferior plant to multiply the superior plant. Several types of grafting are described, including approach grafting, whip grafting, cleft grafting, top grafting, veneer grafting, epicotyl grafting, and budding. Budding is defined as a form of grafting where a bud is inserted into the rootstock and allowed to grow. Different budding techniques like T-budding, patch budding, chip budding, flap budding, and ring budding are also outlined.