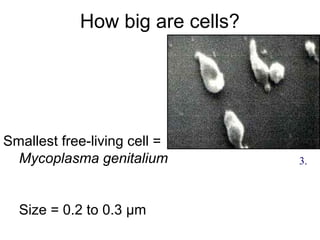
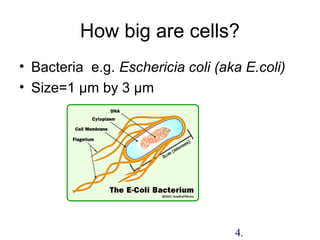
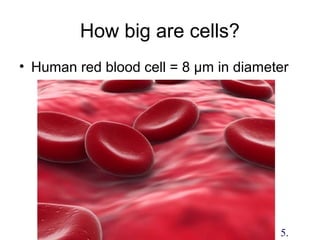
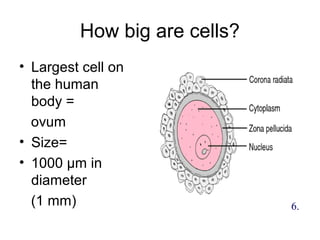
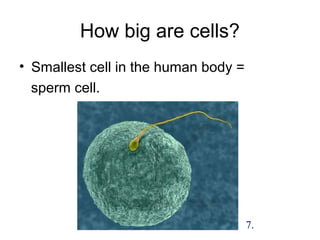
1. The document discusses the cell as the basic unit of life and provides a detailed overview of cell theory and cell structure. It describes key discoveries in cell biology including Hooke's observation of cells in cork and van Leeuwenhoek's discovery of single-celled organisms under the microscope.
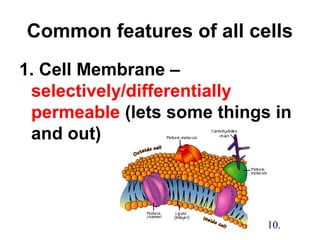
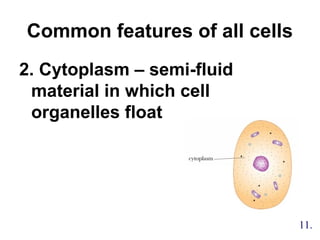
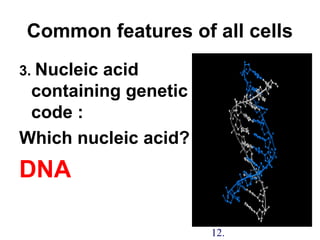
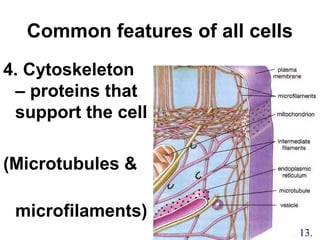
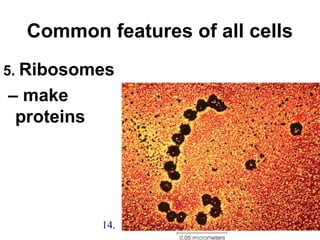
2. The three main points of cell theory are presented: all living things are made of cells, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function, and cells only come from pre-existing cells. Common features of cells like the cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, and organelles are also outlined.
3. Modern additions to cell theory are noted including that cells contain DNA, have similar composition and metabolism, and function