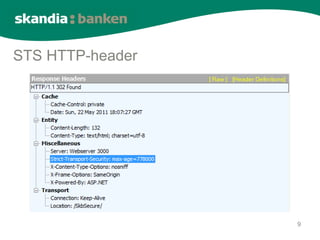
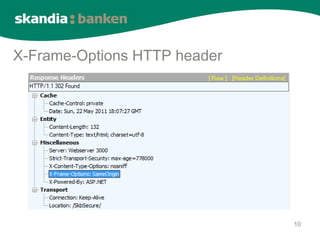
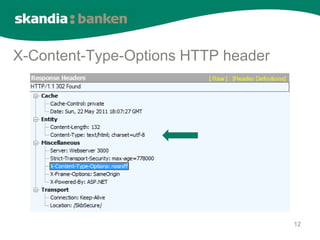
The document summarizes browser security challenges and modern security features. It discusses how the browser enforces the same-origin policy to isolate websites, but how malicious code could turn the browser evil. It then outlines security features like sandboxing, tab isolation, and security headers that browsers implement to minimize damage from compromises and strengthen website security. These features help compensate for website vulnerabilities and block attacks like cross-site scripting.