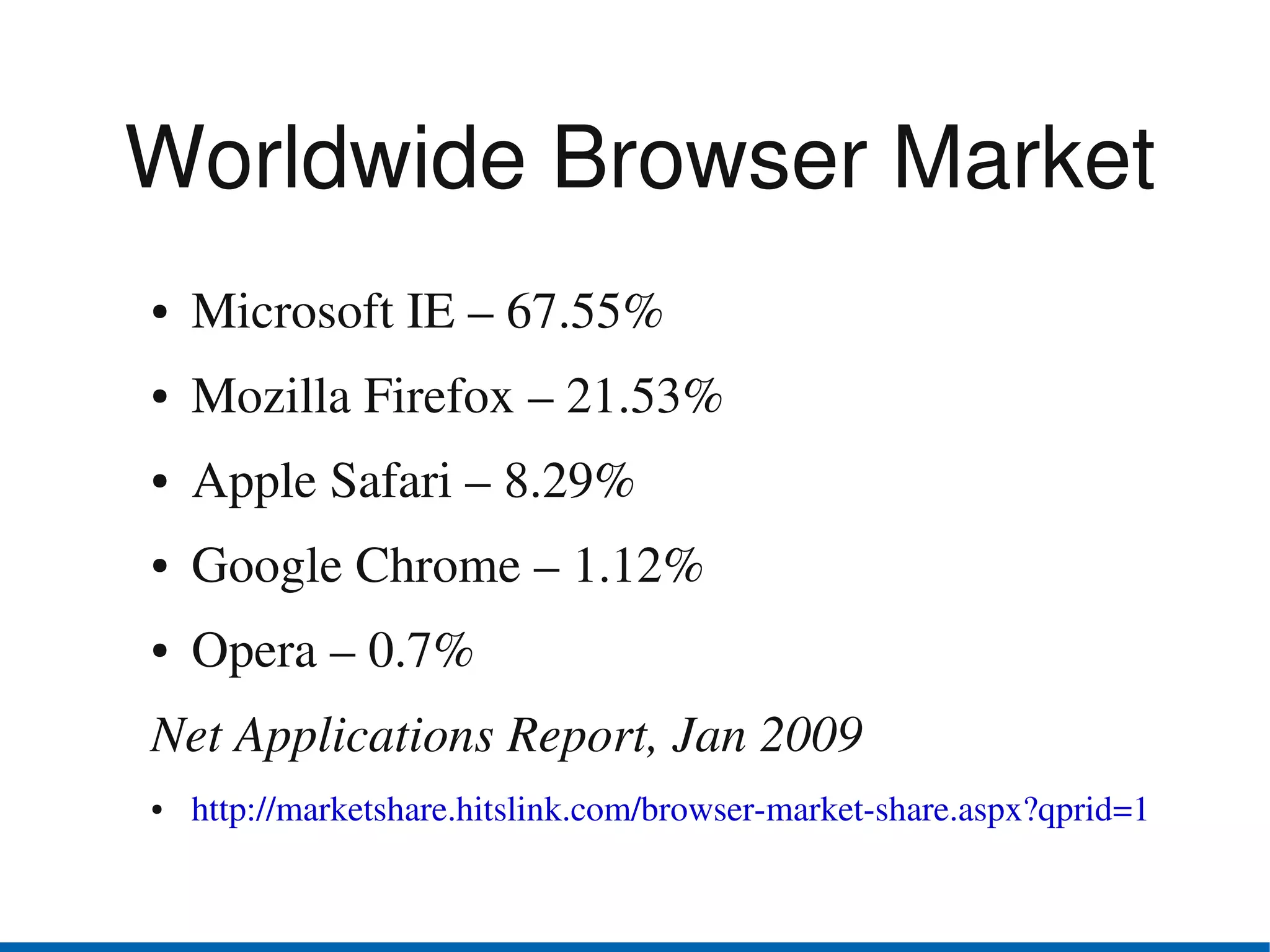
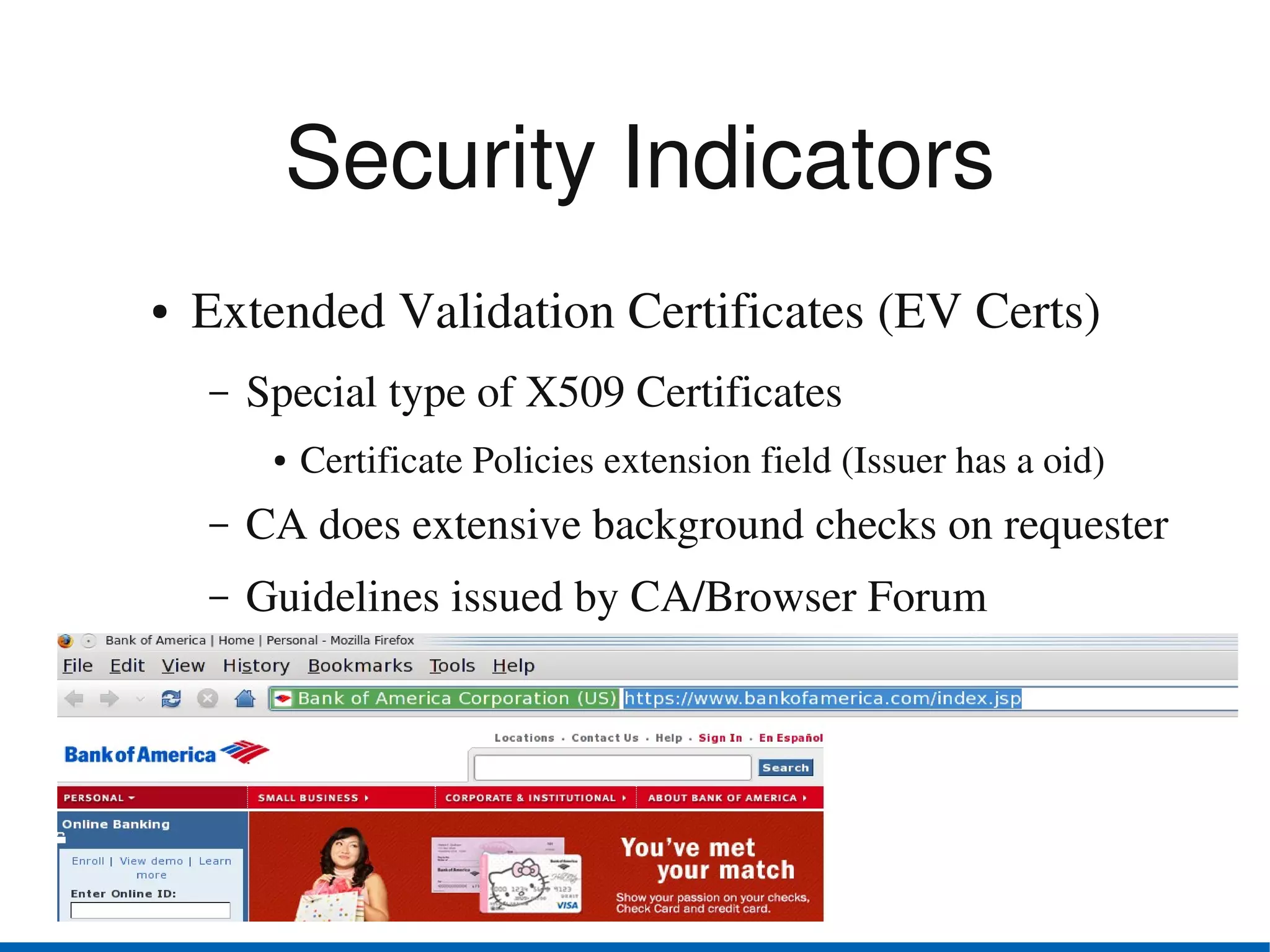
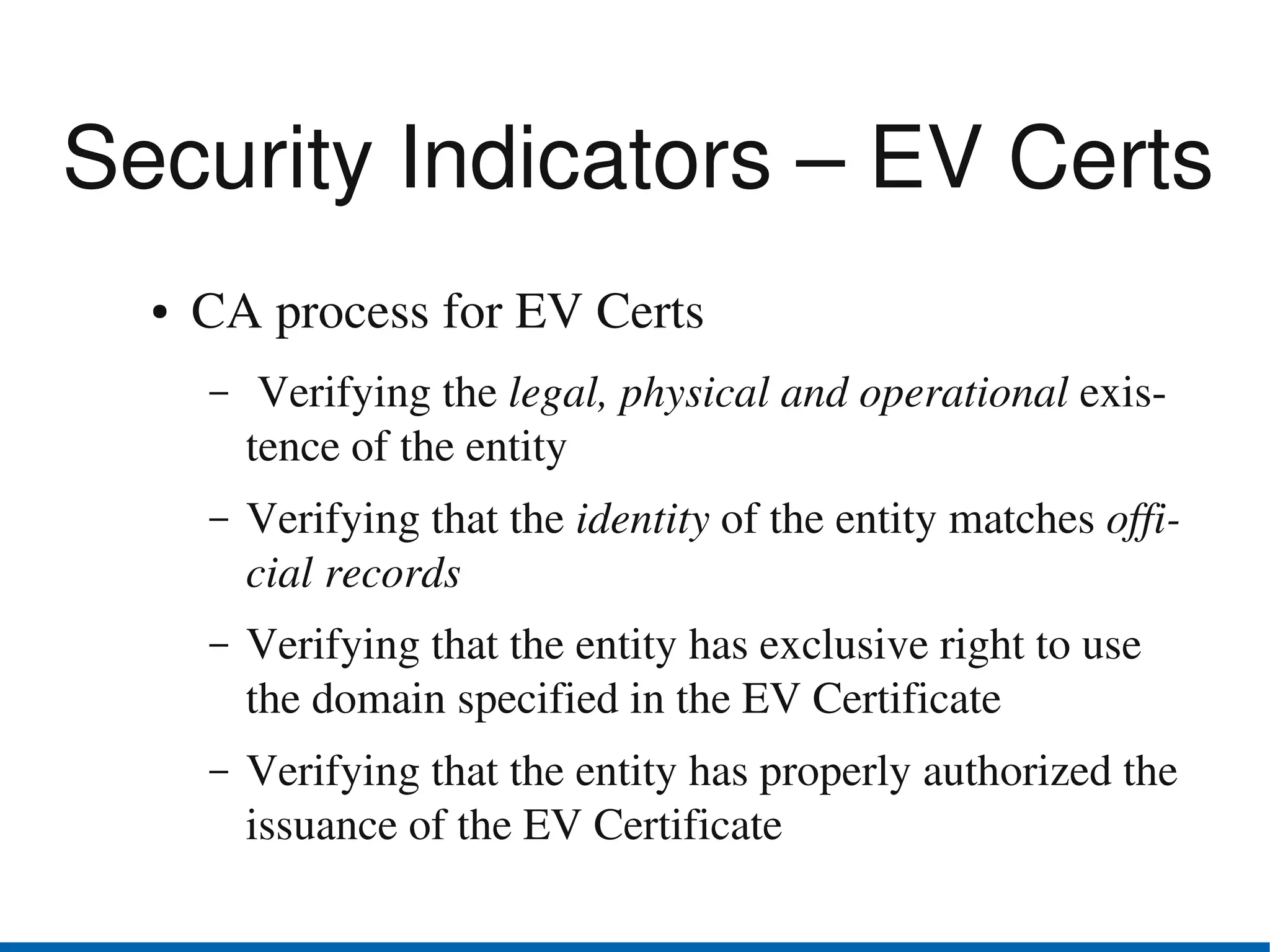
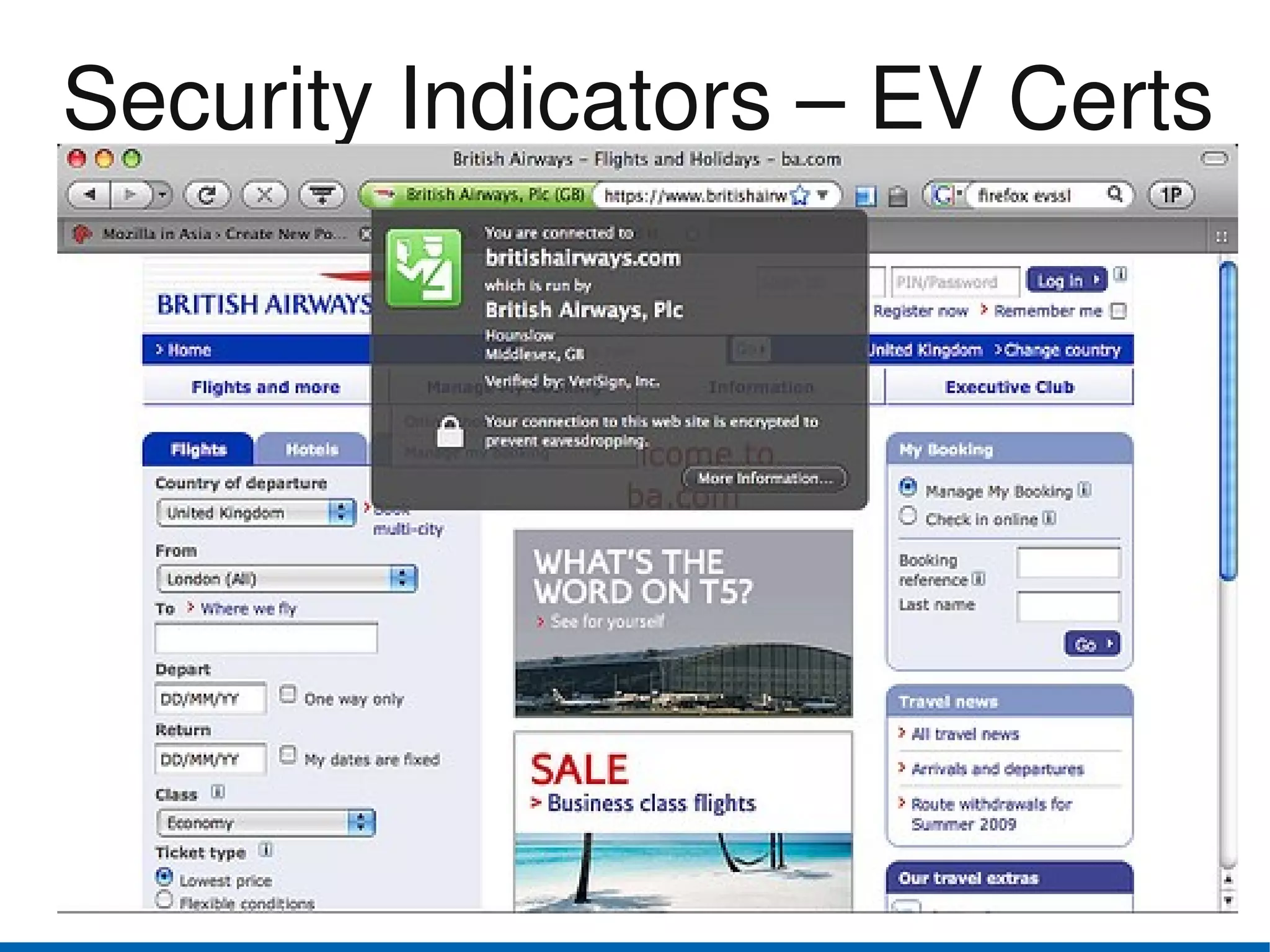
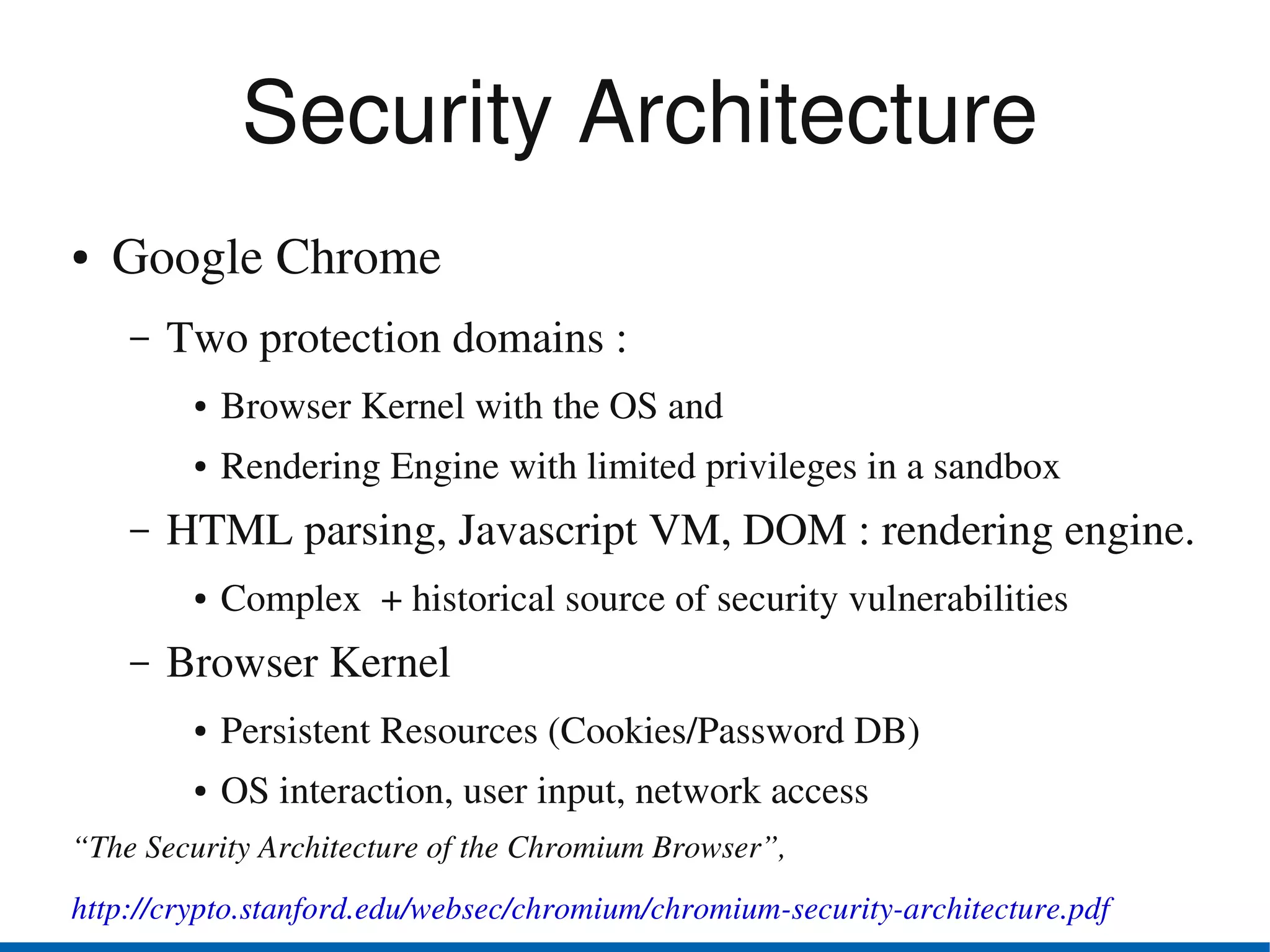
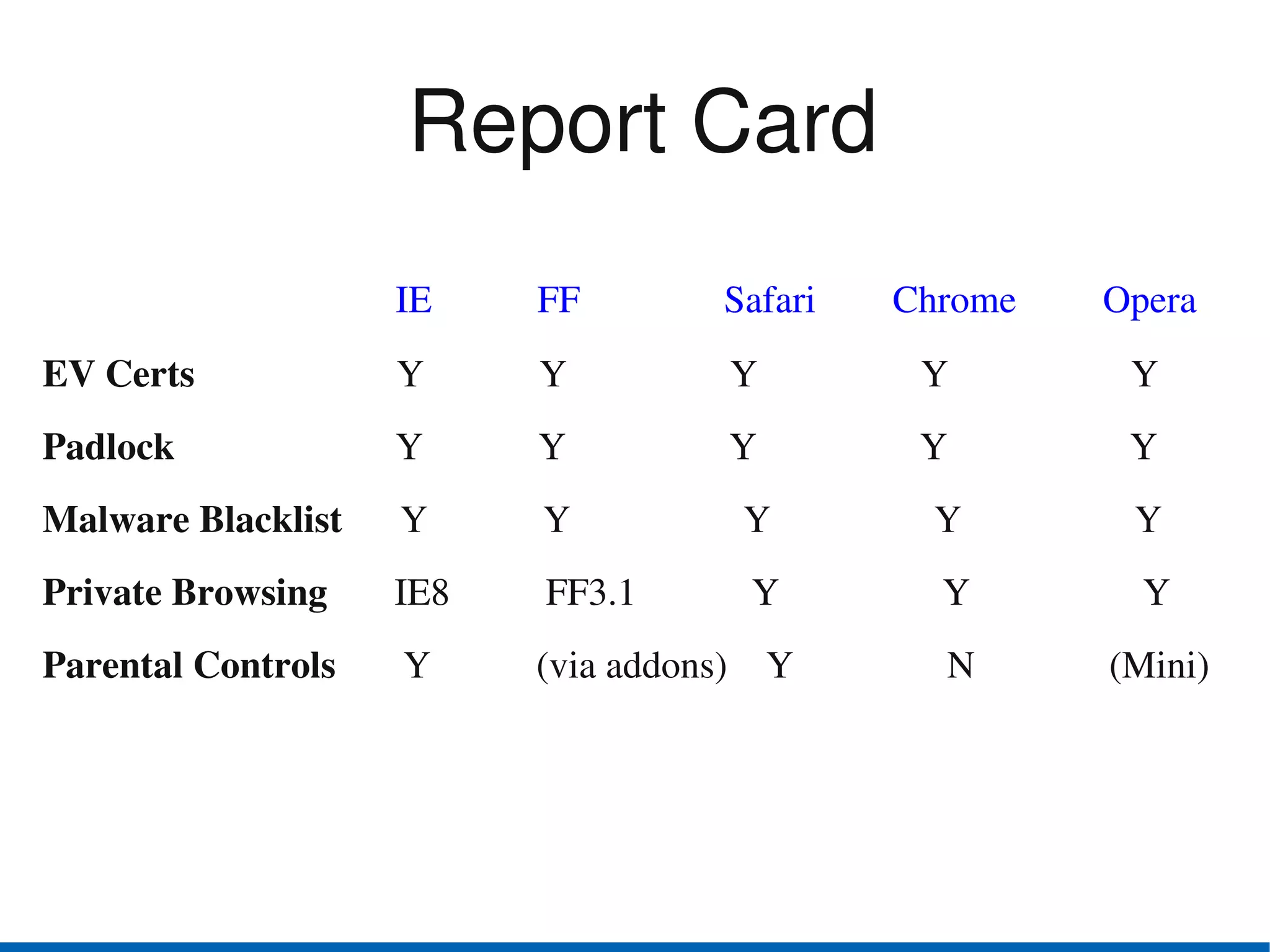
Browser security has advanced in recent years. The top browsers - Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome and Opera - all provide security indicators like green bars for extended validation certificates and padlocks. Google Chrome uses a security architecture with separate protection domains for the browser kernel and rendering engine. Private browsing and parental controls allow for more private web use. The W3C Web Security Context specification aims to standardize security context information presented to users across browsers. Users should exercise caution and use security features of their browsers like disabling plugins by default and blocking third-party cookies.