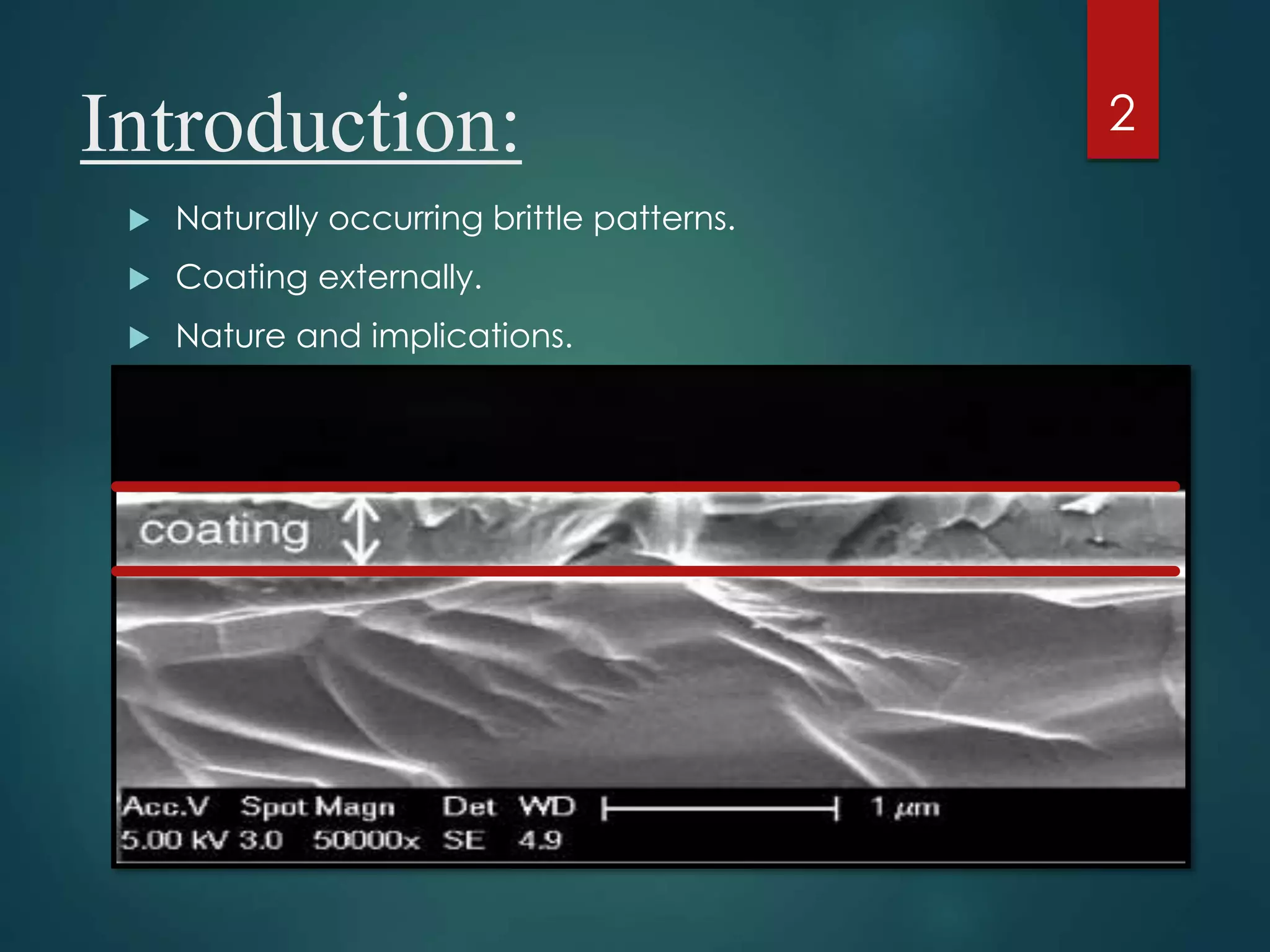
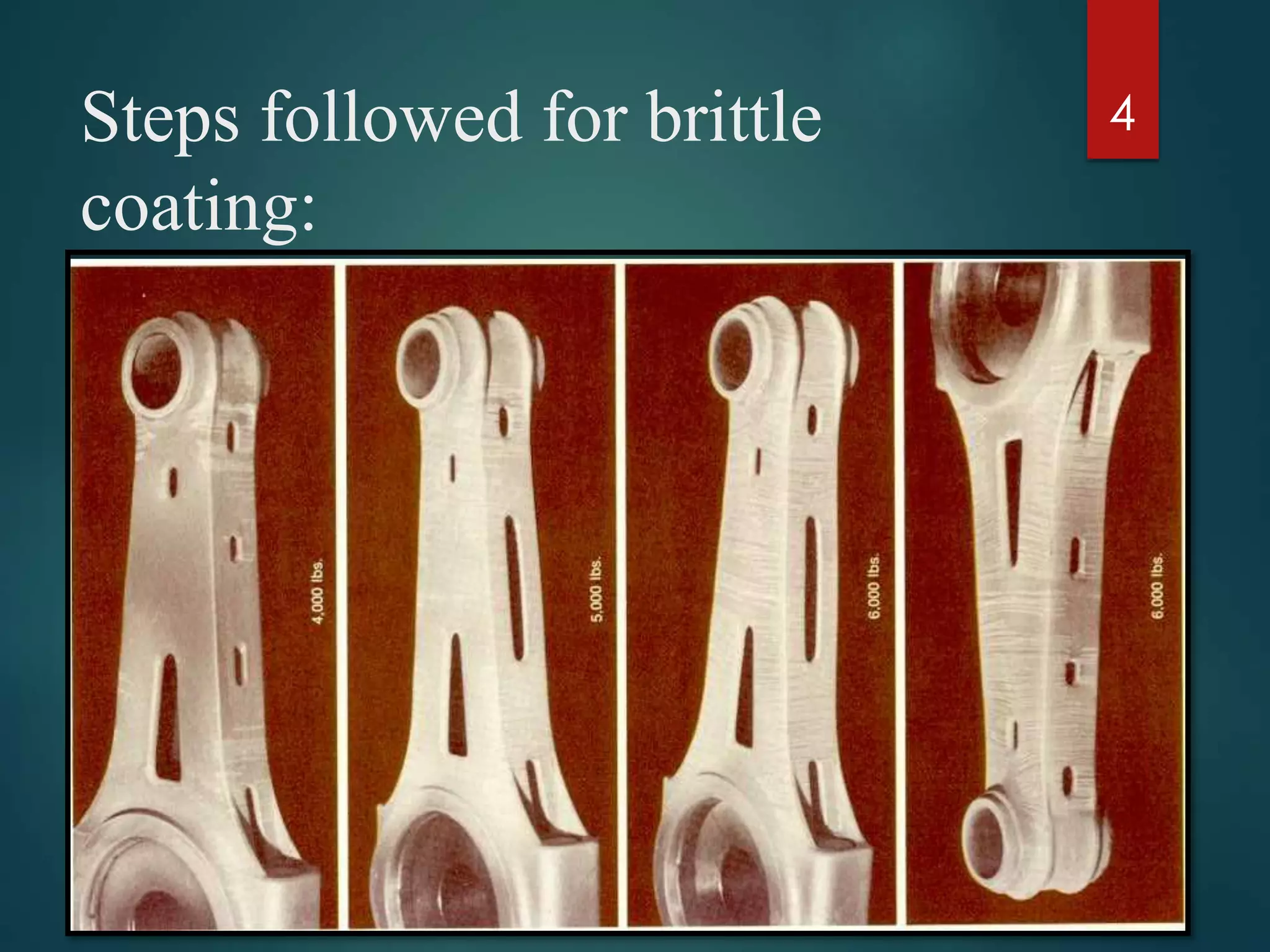
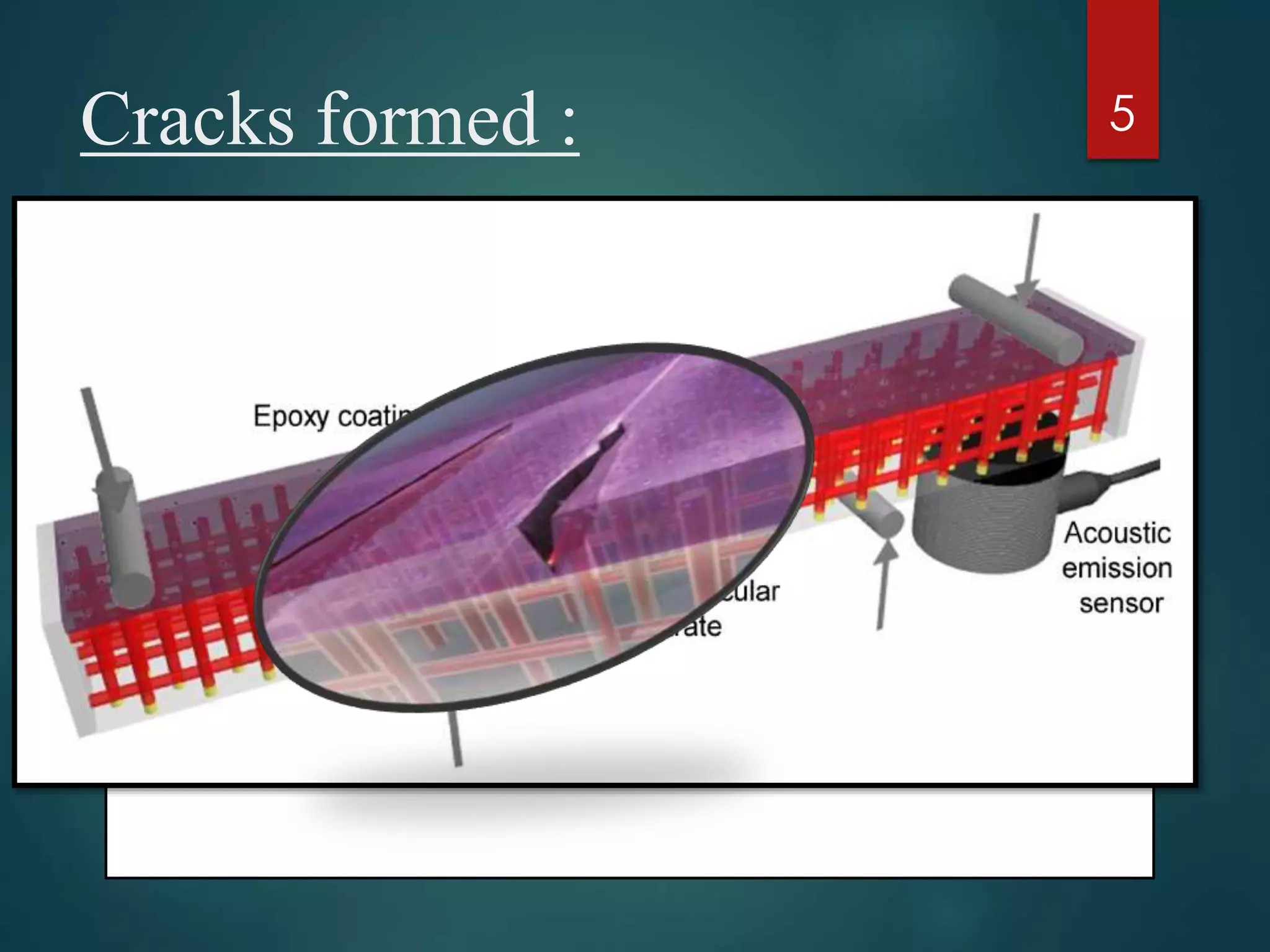
The document discusses brittle coating methods, highlighting their advantages such as providing comprehensive stress data without requiring modeling. It details two types of brittle coatings: resin-based and ceramic-based, including their compositions and temperature sensitivities. The process for applying brittle coatings involves selecting the material, preparing the surface, and analyzing crack patterns after testing.