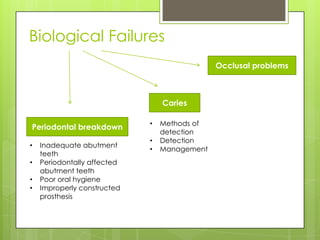
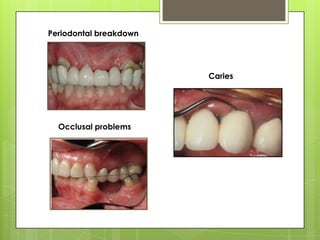
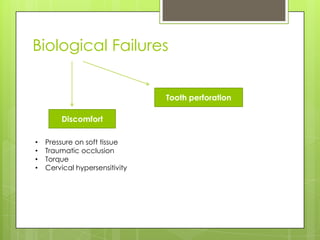
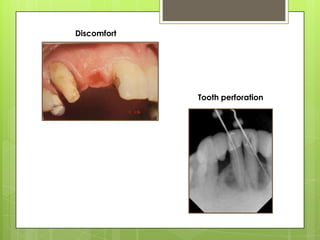
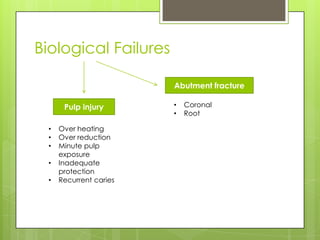
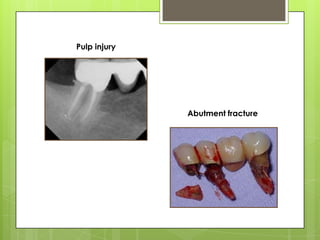
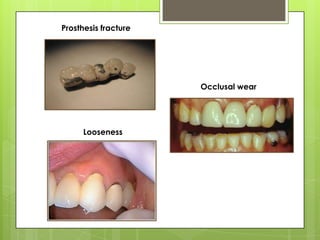
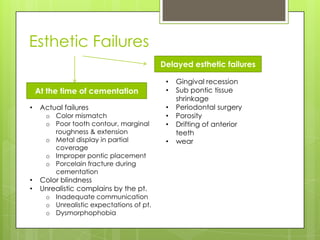
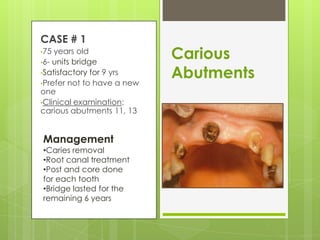
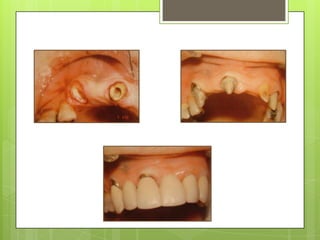
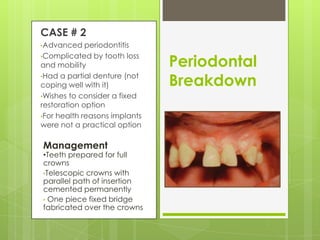
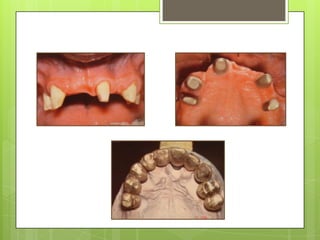
This document discusses bridge failures in dentistry. It identifies the main manifestations of failure as pain, inability to function, dissatisfaction with aesthetics, and other issues. Failures are classified as biological, mechanical, or esthetic. Biological failures include issues like caries, periodontal breakdown, pulp injury, and tooth perforation. Mechanical failures involve looseness, fracture of the prosthesis, and occlusal wear. Esthetic failures occur at cementation or later due to issues like gingival recession or color mismatch. The document provides examples and descriptions of various types of failures and recommends avoiding failures by careful planning, addressing preoperative problems, and designing prostheses to allow for future treatment if needed. It also presents two