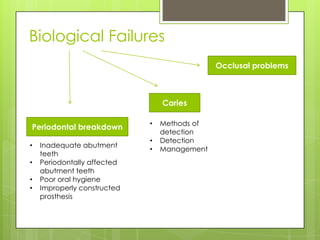
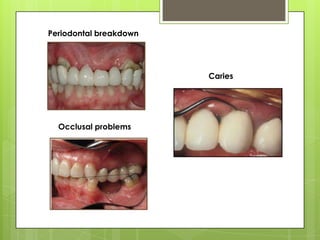
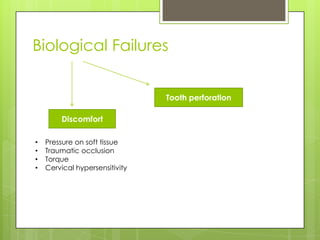
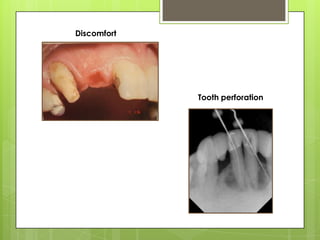
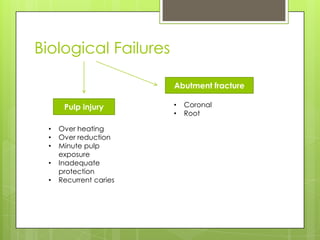
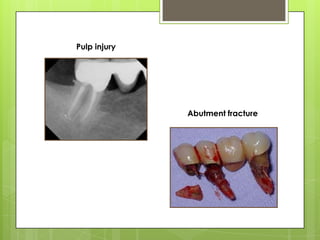
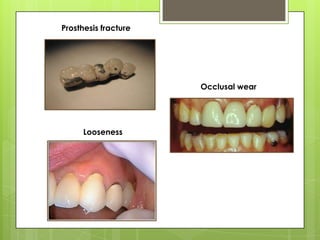
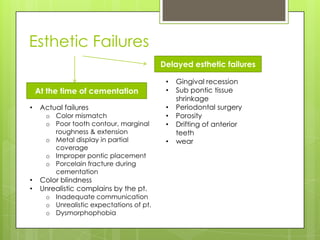
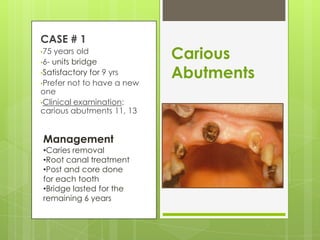
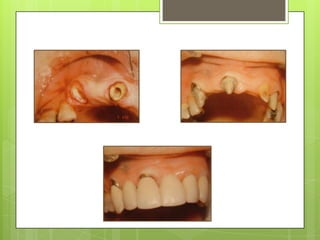
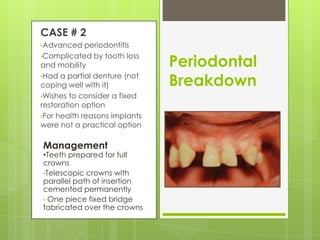
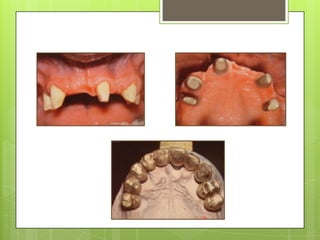
This document discusses types of failures in fixed dental prostheses. It describes biological, mechanical, and esthetic failures. Biological failures include periodontal breakdown, caries, occlusal problems, discomfort, tooth perforation, and pulp injury. Mechanical failures involve looseness or dislodgement, prosthesis fracture, and occlusal wear or perforation. Esthetic failures occur at cementation or are delayed, due to issues like color mismatch or gingival recession. Causes of failure include improper case selection and treatment, inaccurate procedures, and poor maintenance. The document presents two clinical cases of fixed prosthesis failures treated by addressing carious abutments and using telescopic crowns for advanced periodontitis.