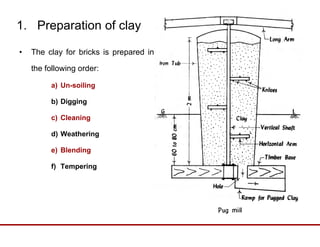
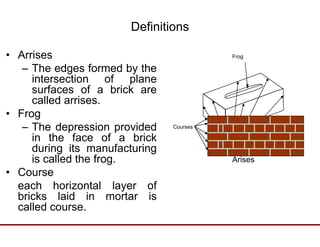
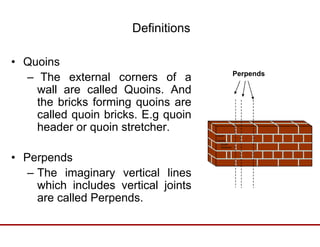
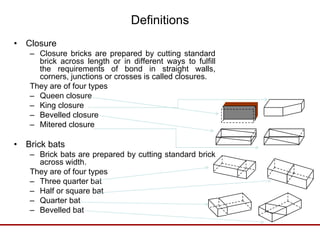
Brick has been used as a building material for centuries due to its durability, strength, reliability and low cost. It is made by preparing clay through processes like blending, tempering and molding into bricks, then drying and burning. The key ingredients in clay that give bricks their properties include alumina, silica, lime and iron. Bricks are classified by their positioning in walls, such as headers, stretchers. Other brick terminology includes arrises, frogs, courses, quoins, perpends, closures and bats. Good bricks are table molded, well-burned, copper colored and free from cracks, with uniform shape and size that produces a clear ringing sound.