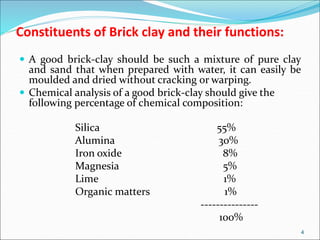
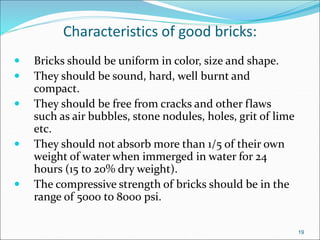
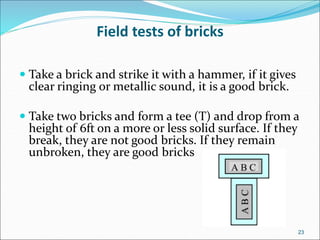
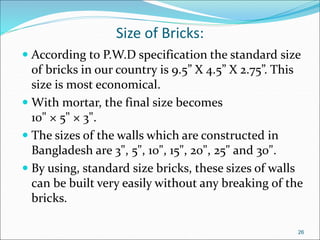
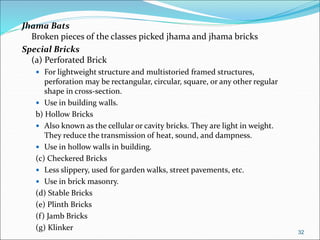
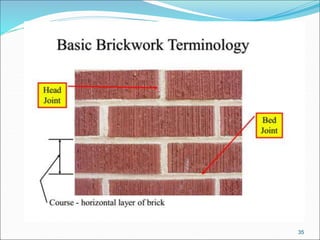
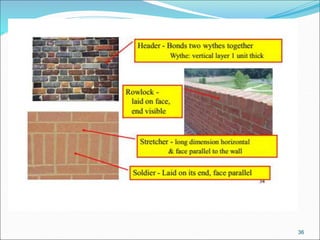
Bricks are artificial stones made from clay that harden when heated to high temperatures. The quality of bricks depends on the clay composition and manufacturing process. Good brick clay contains silica, alumina, iron oxide, magnesia, lime, and organic matter in specific percentages. The constituents impact properties like plasticity, density, color, shrinkage, and fusion. Bricks are tested based on hardness, strength, water absorption, and efflorescence. Standard bricks measure 9.5x4.5x2.75 inches and are classified by quality and use in construction.