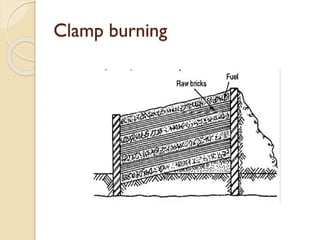
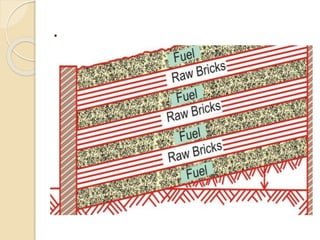
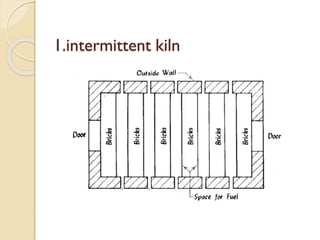
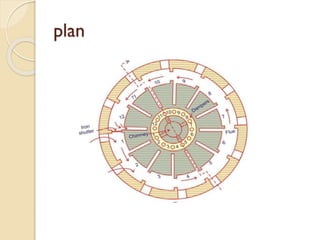
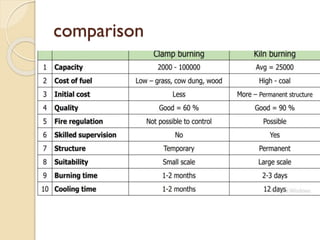
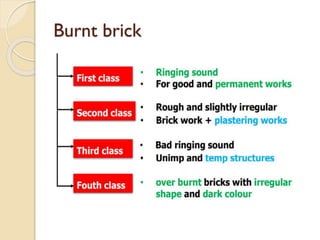
This document discusses the manufacturing process of bricks. It involves preparing clay, moulding bricks, drying them, and then burning them in clamps or kilns. Burning is an important stage that gives bricks hardness and strength at a temperature of around 1100°C. Bricks can be burned in clamps or kilns, with kilns allowing for more uniform burning. Good bricks are uniformly shaped and sized, give a clear ring when struck, and meet standards for water absorption and crushing strength.