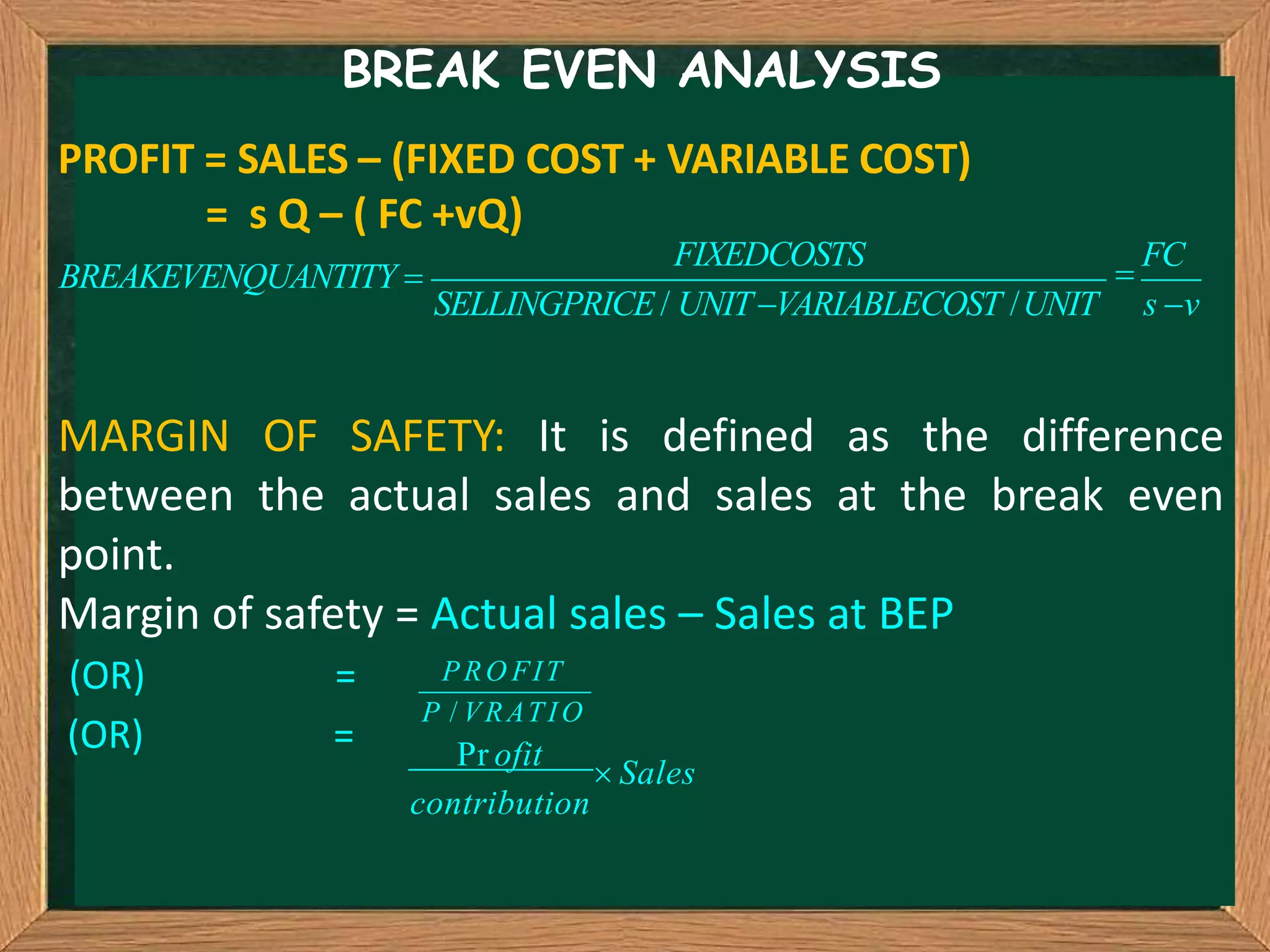
Break even analysis determines the level of production and sales where total revenue equals total costs, resulting in neither a profit nor a loss. The break even point is shown on a break even chart, which plots total costs and revenues. Key terms include fixed costs, variable costs, break even quantity, margin of safety, and profit. Formulas show how to calculate break even point, profit, and margin of safety using selling price, variable costs, fixed costs, and production quantity.