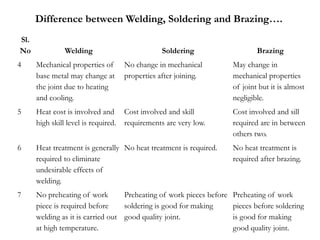
Brazing is a metal joining process where a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base metals is heated to bond them. The filler metal melts and flows into the joint by capillary action without melting the base metals. Proper clearance must be provided in the joint design for the filler metal to flow effectively. Common filler metals include copper, aluminum-silicon alloys, and silver alloys. Brazing allows for dissimilar metal joining and produces stronger joints than soldering but with less distortion than welding.