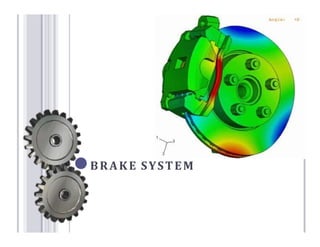
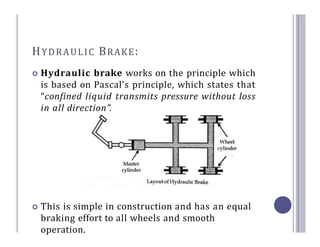
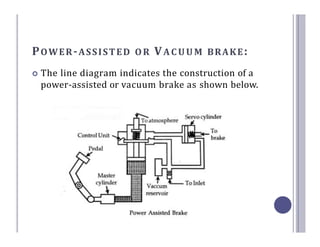
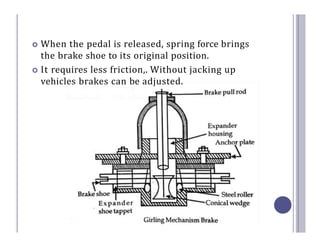
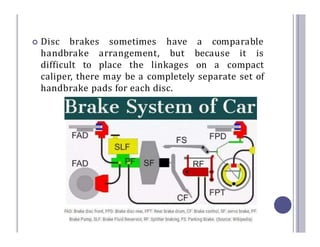
The document defines and describes the various types of brake systems used in automobiles. It discusses mechanical, disc, hydraulic, power-assisted, air, and hand brake systems. The hydraulic brake system is the most common, using fluid pressure to slow wheels. When the brake pedal is pressed, fluid pushes brake pads against a disc or drum, converting kinetic energy to heat and slowing the vehicle. Master cylinders control fluid pressure to wheel cylinders for balanced braking on all wheels. Power-assisted and air brakes use vacuum or compressed air to augment braking force. Hand brakes provide independent parking capability.