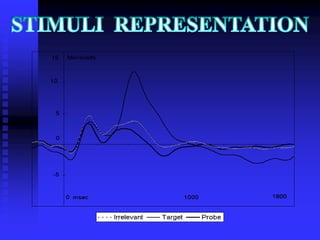
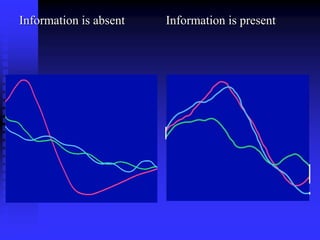
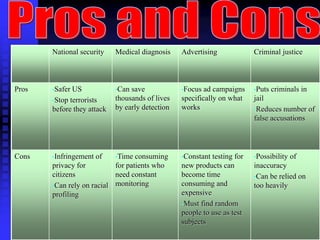
Brain fingerprinting is a technique developed by Dr. Lawrence Farwell in 1999 to determine what information is stored in a person's brain. It works by measuring brain wave responses, specifically the P300 wave, to visual or audio stimuli. A sequence of target, irrelevant, and probe stimuli are presented while monitoring brain waves to see if a greater response occurs to probes related to information stored in the memory. The technique has potential applications in national security, medical diagnosis, advertising, and the criminal justice system, though concerns exist around privacy infringements and potential inaccuracy.