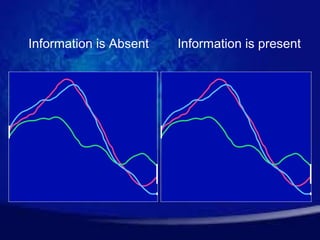
Brain fingerprinting is a technique that uses electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain waves and determine if information about a specific event is stored in a person's brain. EEG sensors are attached to the head to measure brain responses to probes, targets, and irrelevant stimuli related to an investigated event. If the brain responds differently to targets, it suggests the person has information about the event stored. The technique has been used to identify terrorists and has a reported 100% accuracy rate in US government tests. It measures brain activity rather than eliciting a subjective response like a polygraph.