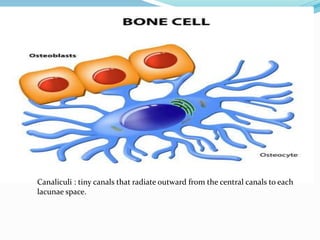
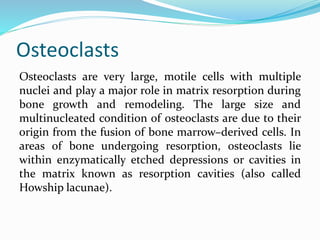
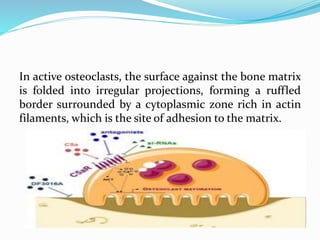
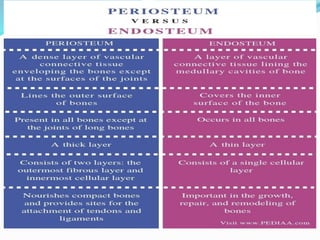
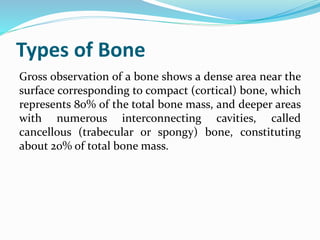
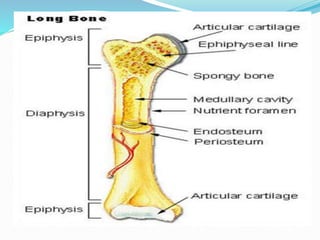
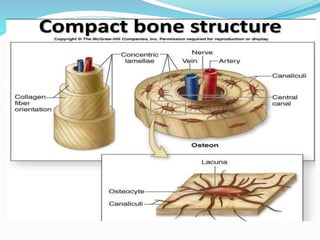
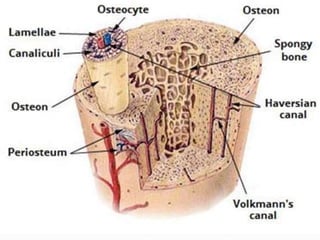
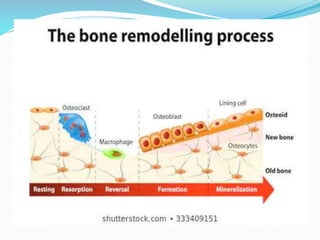
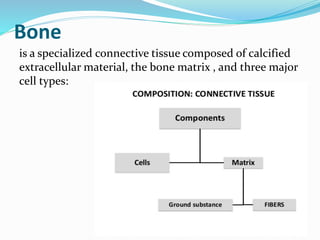
Bone is a specialized connective tissue composed of cells and an extracellular matrix. There are three main cell types in bone: osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts. Osteocytes are found embedded in the bone matrix, osteoblasts synthesize the bone matrix, and osteoclasts break down and resorb bone. The document describes the structure, composition and functions of bone as well as the roles of the different bone cells. It also discusses bone remodeling which involves continuous resorption and formation to replace old bone.






![Osteoblasts also release membrane- enclosed matrix
vesicles rich in alkaline phosphatase and other enzymes
whose activity raises the local concentration of PO4 −
ions. With high concentrations of both calcium and
phosphate ions, these vesicles serve as foci for the
formation of hydroxyapatite [Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]
crystals, the first visible step in calcification. These
crystals grow rapidly by accretion of more mineral and
eventually produce a confluent mass of calcified
material embedding the collagen fibers and
proteoglycans.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bone-histology-200612081233/85/Bone-histology-8-320.jpg)