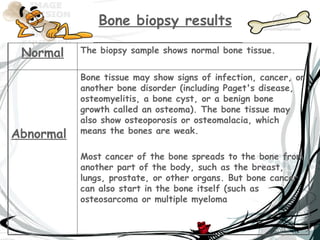
The document discusses bone biopsy and decalcification. A bone biopsy is performed to remove a small bone sample, which is examined under a microscope to diagnose bone disorders like cancer or infection. It can be done with a closed needle biopsy or open biopsy requiring anesthesia. Bone decalcification involves removing calcium from bone samples using acid solutions, ion exchange resins, or chelating agents so the bone is flexible and can be examined microscopically. Common decalcifying agents discussed are nitric acid, formic acid, and EDTA.