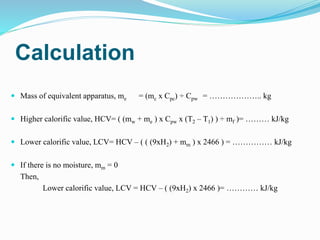
A bomb calorimeter is used to determine the calorific value of solid and liquid fuels. It consists of a thick-walled stainless steel bomb placed in a water bath inside an insulated container. A known mass of the fuel is burned in oxygen inside the bomb, causing the temperature of the surrounding water to increase. The temperature change and the mass of water are used to calculate the heat released during combustion, from which the calorific value of the fuel can be determined. Corrections are made for heat losses and other factors to obtain an accurate calorific value. While it provides accurate measurements, the bomb calorimeter cannot test gaseous fuels or reactions that are too slow or vigorous.