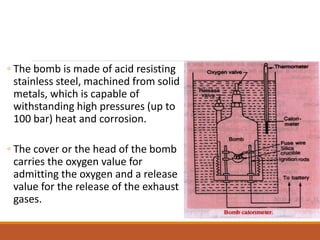
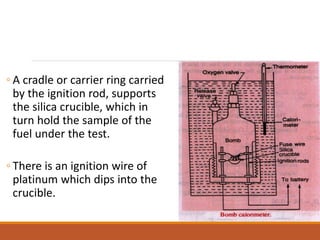
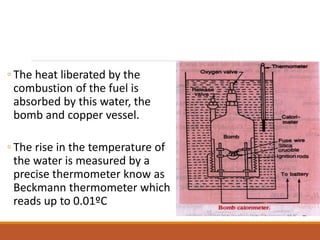
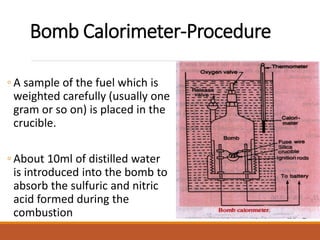
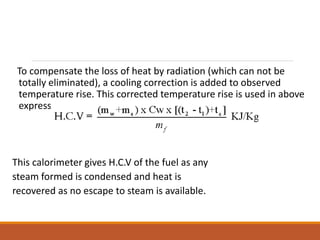
The document describes the bomb calorimeter method for experimentally determining the higher calorific value of solid and non-volatile liquid fuels. A known mass of the fuel is burned inside a strong, sealed bomb submerged in a known mass of water. The temperature rise of the water absorbs all the heat from combustion. Calculations using the temperature rise and masses then allows determining the calorific value of the fuel in kJ/kg. The document provides details of the bomb construction, procedure, and calculations.